Do you suspect your phone is being monitored? Identify the top signs along with the proven methods to know if your phone is tapped and protect your privacy immediately:
If you’re worried that your phone may be tapped, it’s important to know the warning signs before jumping to conclusions. Unusual battery drain, strange noises during calls, unexpected data usage, or unfamiliar apps can sometimes indicate unauthorized monitoring.
In this section, I will explain how to know if your phone is tapped, outline the common signs to look for, and share practical solutions you can use to protect your device and restore your privacy.
Table of Contents:
- Is Your Phone Tapped? Find Out Signs & Solutions
- What to do When Someone is Listening to Your Calls
- Top Signs to know that your Phone is tapped
- Сodes to check if the phone is tapped or hacked
- Which Phones are Easiest and Most Difficult to Tap?
- Top Ways to Know if Your Phone is Tapped
- Technologies to Detect When a Phone is Tapped
- Best Tools to Monitor & Avoid Phone Tapping
- How to Avoid Your Phone Being Tapped
- Why and Who May Be Tapping Your Phone? (Legal in the U.S.)
- Penalties (Under U.S Law) for Phone Tapping
- How People are Vulnerable to Phone Tapping
- Are There Any Advantages of Phone Tapping
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Is Your Phone Tapped? Find Out Signs & Solutions

Here are the top 5 signs to alarm you that your phone is being tapped:

- The battery depletes unusually, unexplained, and unaccountably fast.
- Unexplained and unusual surge in battery consumption.
- Phone calls have strange background sounds, echoes, or clicks.
- The device heats up for unexplained reasons.
- Sudden reboots, freezes, or crashes.
What to do When Someone is Listening to Your Calls
Enlisted below are the steps to follow if someone is listening to your phone calls:
- Turn on Airplane mode and begin the investigation by, for example, updating the OS and programs to see if unusual battery consumption stops. Scroll the app list and check each, and remove spyware from the phone, or uninstall or block suspicious ones. Remove app data background, change account passwords, uninstall VPN, or use trusted ones.
- Factory reset the device if battery usage continues.
- Run a forensic examination if the OS and app update, factory reset, and the above strategies do not work.
- Inform carriers through writing.
- Report the case as a criminal case to the police.
Top Signs to know that your Phone is tapped
Here are 20 pieces of advice for determining whether someone is eavesdropping on your phone conversations, along with recommended actions to take.
The sign below (with three little paragraphs each) explains why the sign is suspicious, how to verify the sign, and what to do with the sign.
1. Unaccounted Fast Battery Depletion

[Via android.com]
Why it is important: When your battery runs out much quicker than usual, that indicates background processes or spyware that is continually accessing the CPU, radio, or the microphone. These days, malicious applications can silently run in the background and burn power.
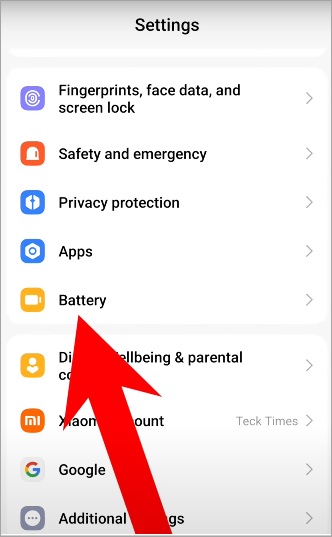
How to check battery usage in settings (iOS or Android) to identify apps that are running:
An unknown or system-level application may draw more power than usual, so write notes and contact a reliable mobile-security scanner or the support of the device manufacturer.
Next steps: Immediately update your OS and programs, scan with a reputable antivirus/anti-spyware to remove spyware from the phone, revoke unnecessary permissions to apps, and think about turning on Airplane Mode during the investigation.
In case the suspicious use continues, make back-ups and do a factory reset, or have a professional run a forensic examination.
2. Large Peaks in Phone Data Consumption
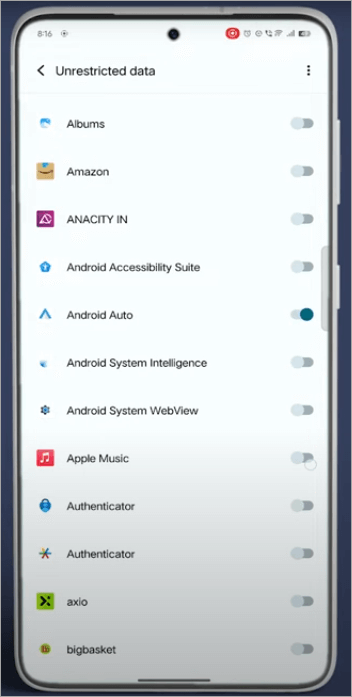
Large or unaccounted peaks in phone data consumption are explained below.
Why it is important: Spyware and remote-monitoring tools often upload recordings, logs, or location dumps, which are reflected as abnormally high cellular data usage despite not necessarily streaming or downloading anything.
How to verify: Check the month-to-month data of your carrier account and in the data-usage settings of your phone, which apps consumed the most data, and have data transfers happened when the phone was not in use.
Possible actions: include force-stopping or uninstalling suspicious apps, blocking background data on applications you do not trust, changing your account passwords, only using a VPN provided by a reputable company, and notifying your carrier in case of unexplained traffic in the radio layer.
3. Phone Calls Have Strange Background Sounds
Phone calls with strange background sounds, echoes, or clicks are one of the signs of Phone Tapping.
Why this is important: If there are weird noises on phone calls or unwanted artifacts such as clicking, echoes, or static, there is a higher possibility that the phone call is being intercepted or there are automated call forwarding settings activated. These sounds initially were used to identify when a call is being bridged or recorded.
How to confirm: Make calls on a different phone and network; note when and where the interference happens and whether it correlates with specific numbers, places, or times; then you can also call the technical support of your carrier and have them look into the possibility of call-forwarding or provisioning errors.
What to do: Do not discuss sensitive issues on believed lines if there are weird noises on phone calls, record the exact time of the call and the person called, notify your carrier in writing, and seek the advice of legal counsel in case the interference implies an illegal intercept.
You should report to the police in case of suspicion that a phone tapping crime is ongoing and/or affecting you, and keep evidence such as timestamps and recordings.
4. Overheating of Device Without any Apparent Cause
Why it is important – Continuous overheating may indicate background processes that consume a lot of CPU, like keylogging programs, audio recordings, or ongoing data exfiltration; this may be an indicator of unresolved surveillance software.
How to check:
Android: Use the Developer options (Android battery graphs) / iOS battery graphs) to check which apps are running when the device is hot and to see whether the device gets hot when the screen is off. To check for overheating, turn off the device and observe if it becomes hot.
How to act: Kill suspect applications, update firmware, clear caches, and in case the issue does not vanish, backup and factory-reset; look at having a reputable phone-forensics company examine the phone.
5. Sudden Reboots, Freezes, or Crashes
Why it is important: Spyware or poorly-installed spyware will cause the OS to destabilize and give crashes or reboots; or alternatively, system changes (rooting/jailbreaking) made to put the surveillance in place can cause the device to become flaky.
To verify the issue satisfactorily, check your system logs (Android through ADB, or analytics diagnostics in iOS) or contact vendor support to verify from crash reports; specify whether a particular time or behavior triggers the bad behavior or occurs after a particular action.
What to do: Update your OS/software, uninstall any apps suspected of causing the breach, and delete any device profiles or ADM profiles that are not authorized by you. If instability continues, back up your data and information, and then do a factory reset or visit an authorized repair or forensics service.
6. Unrecognizable Applications:
The importance of this fact is that Stalkerware and various other monitoring tools install elements that can disguise their icons or place themselves under a friendly name, providing consistent access to audio, messages, and location.
How to verify: Look at the list of apps installed on your device currently to check if they are malware or viruses, or indicate any jailbreak signs, such as Cydia or unknown profiles. Also include device-admin apps on Android and on iPhones for this check-up.
Next steps: Make sure to immediately update your operating system and programs on the device. Ensure to also scan with anti-virus and anti-malware tools, revoke all permissions unnecessarily granted to apps on your device, and even consider turning on the Airplane Mode when investigating if your phone calls are being infiltrated.
If the issue is unending, back up your information and data and factory reset the device, or have the device undergo a thorough forensic investigation by professionals or using professional tools.
7. Sent or Dialed Outgoing Texts/Calls that are not Yours:
Why this is important: Spyware can carry the information by sending texts or making calls, and certain intercepting configurations will generate new outbound traffic, which will be hidden – hence a red flag.
How to confirm: Check your call and sms history, review the history of billing by the carrier to see if there are any items you do not recognize, and compare the time with your location or phone possession records; ask your carrier to trace the circuits of origin.
What not to do: Do not change the passwords on your account because you should use multi-factor authentication, call your carrier to turn off suspicious services, and save the records, which may be used later in court by law enforcement officers or legal counsel.
8. Suspicious Pop-ups:
Why it is important: That is the tip of the iceberg; those browser annoyances may contain tracking or credential-stealing modules. Many or most ecosystems meant or made to spy on calls and other user data and information mainly use ad-injection or inject ads onto contents and enforce malicious redirects.
How to confirm: Run a security scan with a reputable vendor, delete browser caches and extensions, and ensure the issue continues in private / incognito mode or when extensions are turned off.
What you should not do: Do not delete malicious extensions, click your browsers to default settings, install ad-blockers and anti-malware tools that are known, and never download APKs or third-party browser extensions that are unknown.
9. Cameras or Microphones indicate on randomly:
Why it is important: When your gadget indicates that there is audio or camera action (indicator LEDs, the orange/green dots on iOS) during times that you are not using the gadget, it could be that apps are accessing the camera or camera surveillance.
How to verify: Check that your microphone and camera permissions are active, scan the apps that are enabled to run in the background, and monitor the system indicators when idle; you can consider the green or orange activity dots that appear on an iOS device to be clear indicators.
What to do: Turn off microphone/camera permissions to suspicious apps, delete apps that need access to unnecessary information, and, in case you suspect you are being spied on constantly, power-cycle the device, back up, and factory reset, and consult the authorities or forensic experts.
10. Bizarre texts found in the SMS, coded characters or links:
Why it is significant: Some links can download stalkerware or issue commands to pre-existing spyware; coded messages may be a part of command-and-control signaling.
Why is it significant: Following some links leads to the downloading of stalkware, or it can issue commands to one that is already existing application on the device; coded messages can be used as part of command-and-control signaling.
How to confirm: Refuse to click just any other link you come across or are sent, save the message (take a screenshot that can be forwarded to a secure email and forward it), use a safe scanner to scan the links you come across on a different computer and ask on the security forums or ask the antivirus vendors to provide the matching signature.
What to do: Block the sender, report the SMS to your carrier, scan with a malware, and in case you think that you have already opened such links, change passwords, and maybe do a factory reset or ask a professional to do it.
11. Password Manipulation:
Why it is important: Including the possibility of attackers having remote control, or stealing authentication tokens through compromising their devices, informers of your online accounts displaying unauthorized changes.
How to verify: Check the account activity pages (Google, Apple ID, and email providers) to all new account logins or device approvals; check the history of recovery email/phone and session.
What to do: The first thing to do is get accounts using new, unique passwords, enable your two-factor authentication method, especially the hardware keys, and ask your service providers to delete any suspicious sessions on the device. Keep a record of law enforcement.
12. Creepy Find my device or Location-tracking Apps:
Why it matters: Unauthorized location sharing or the addition of a new device may imply that one is being followed or that an account has already been configured on their phone.
How to verify: Check your Google account through its Device activity, Apple Find My settings, and location permission; you can authenticate all the approved devices and remove the unfamiliar ones.
Turn off the feature to share your location, change the passwords of your accounts, remove any devices you deem suspicious, and check whether there are background location access permissions enabled/allowed on any third-party apps. If call tracking continues, notify your carrier or get help from a specialist.
13. Abnormal system or Carrier Configurations Altered (voicemail, call forwarding):
Why it is important: A malicious user can automatically activate call forwarding or voicemail, or this may occur due to a poorly set-up intercept.
How to verify: Dial carrier codes or check your carrier’s call-forwarding settings in the phone app; or call your carrier to verify that call forwarding is being implemented at a network level.
What to do: You may consider turning off call forwarding if it is not necessary, re-establishing your carrier account PINs, requesting an audit on the carrier provisioning for your device, and launching complaints with the FCC and local law enforcement while assuming unauthorized access to network-level controls.
14. Your device indicates that it is rooted or Jailbroken when you did not do so:
Why it is important: Rooting or jailbreaking disables major OS protectors and is often a condition required to install intrusive surveillance software. This is very suspicious when your equipment is attacked in such a manner.
How to confirm: Check if there are any jailbreak apps such as Cydia on iOS, check that you do not host any unauthorized package managers on your device or superuser binaries on Android; use vendor support tools or secure scanners to verify this.
What to do: In this case, never try to jailbreak your phone unless you really know what you are doing or have expertise in it, and before you do, ensure to back up all important information and data and update or re-install official firmware, or to otherwise take your device to a professional for repair. Consider also closing your accounts and passwords.
15. Unpredictable Pop-up requests of Administration or Access Permissions:
Why it is important: malicious apps may take advantage of the accessibility and app permissions by often demanding these permissions in order to carry out a hidden keylogger or screen recording.
How to verify: Check app permissions and the list of device admin apps: apps that have redundant access or administration permissions can be considered suspect.
What to do: Revoke permissions on the app, install the app, and do a security scan; an app may fail to uninstall because of the use of an administrator account, in which case you should revoke the administrator and uninstall the app.
16. There was a drop in Performance and a slowing down inexplicably:
Why it is important: Continuous undercover action – data capture, encryption, or exfiltration – loads the resources of the phone and decelerates everything, and leaves it angry.
How to check: You can employ official tools from Android and iOS, which can be used for performance-monitoring tools (Android Developer options, iOS diagnostics) to check CPU usage and draining of memory, while comparing to a known safe base.
Action needed: Close background applications, remove suspicious software, update the operating system, and in extreme cases, back up, wipe, and restore to a clean state.
17. Surprising LED/screen Activity when Idle:
Why it is important: Check for where the screen wakes up unusually or for unusual lights up because they may signify that certain spyware may be turning on sensors to wake up the screen or light LEDs and take a reading or send.
How to confirm: Have a look at the wake logs and all permissions to use wake lock (Android) and most recently used apps; monitor when the screen is turned on and by which process.
What my action is: Turn off wake-lock permissions with shady apps and uninstall them, and you might want to do a factory reset in case of behavior persistence.
18. Constant Security Warnings or Messages that your Account has been accessed:
Why it is important: The constant alert of the log-in process can mean that a person is under investigation or uses tokens; a series of alerts, along with the device’s peculiarities, is very suspicious.
How to verify: Look at the pages of active internet activity of significant accounts, delete questionable sessions, and be able to monitor device lists of unfamiliar machines or IP addresses.
What should be done: First of all, change passwords (long, strong), activate strong two-factor authentication (use a hardware key, when possible), and monitor all available sessions and authorized applications.
19. You discover Bizarre files, Tapes, or even logs on the Machine:
Why it is important: Hidden recordings or logs are the smoking gun to spying; finding them could be emotional, but they will provide you with evidence that you can keep.
How to check: Don’t handle it, take timestamps, screenshots, even a read-only copy; then call a professional digital forensics service to maintain chain-of-custody.
What to do: The first step is to save the evidence right away, do not use the device anymore, and call the police and a lawyer, as these objects are the primary issue when it comes to criminal or civil proceedings.
Сodes to check if the phone is tapped or hacked
Below are phone forwarding codes to help you know if your phone is being tapped through diverting calls to other places, for instance, when it is offline or unreachable.
| Purpose | Phone forwarding codes to check if your phone is being tapped | What It Shows |
| Check Unconditional Forwarding (all calls) | *#21# | Shows if all incoming calls are forwarded to another number. |
| Check Forwarding when Busy | *#67# | Shows if calls are forwarded when your line is busy. |
| Check Forwarding when Unanswered | *#61# | Shows if calls are forwarded when you don’t answer. |
| Check Forwarding when Unreachable | *#62# | Shows if calls are forwarded when your phone is off or out of service. |
| Check all Forwarding Settings at once | *#002# | Displays any active forwarding rules and may cancel all if supported. |
| Check your IMEI (for security record/reference) | *#06# | Shows your device’s IMEI number (unique ID, useful if you report issues). |
Which Phones are Easiest and Most Difficult to Tap?
Android phones running on older versions, such as Android 7 and below, are notoriously vulnerable to compromise due to their lack of access to the latest security updates and weaker permission systems.
iPhones that have been jailbroken and Android phones that have been rooted are much more vulnerable, as the protective sandbox is also intentionally removed, providing attackers with a direct route into system-level surveillance.
However, the recent iPhones running on iOS 17 and flagship Androids such as Pixel or Samsung Galaxy feature monthly patches and are therefore more difficult to tap because of the secure enclaves utilized on them, due to encrypted storage, and stricter code-signing.
But even those high-end devices are not unreachable; advanced spyware such as Pegasus has been reported to circumvent them through zero-click attacks.
Top Ways to Know if Your Phone is Tapped
Here are some of the top ways in which your cellphone could be spied on.

1. Carrier Provisioning Exploits
The trick to it: Hackers can compromise the provisioning systems of your carrier, which is the back-end infrastructure that provisions SIM cards, routing of calls, and voicemail, to either silently clone your SIM or divert calls and text messages.
How to spot: One red flag is the appearance of unfamiliar carrier settings updates all at once, you are roaming, or you are receiving an SMS provisioning status message.
Also, make sure that your carrier assures you there have been no SIM swaps or a revision of your provisioning details (just call the customer service and enquire). Phone-hacked text messages may fail to deliver at all or have huge delays.
2. Rogue or Rogue Cell Towers (Stingrays/IMSI Catchers)
The methodology: The police and thugs occasionally deploy mock cell towers that pretend to be real towers, stealing communications, text messages, and other metadata.
How to identify: Spoofing of cell towers can be identified on a mobile phone by unusual battery exhaustion and/or consumption on the device, automatic reduction of network to the lowest 2G network, or frequent drop in calls in certain locations. Special applications or gadgets that read tower legitimacy can verify possible suspicious activity.
3. Spyware Software on the Computer
How it works: A stalker or a hacker physically installs spyware on your phone, usually as an innocent utility or by changing settings. After being installed, it records the keystrokes, microphone feeds, and GPS.
How to spot it: Check your apps you do not remember downloading, permissions (microphone, camera, and location in particular), and run antivirus software, such as Norton or Kaspersky, to highlight stalkerware.
4. Zero-Click Attacks Remote Exploits
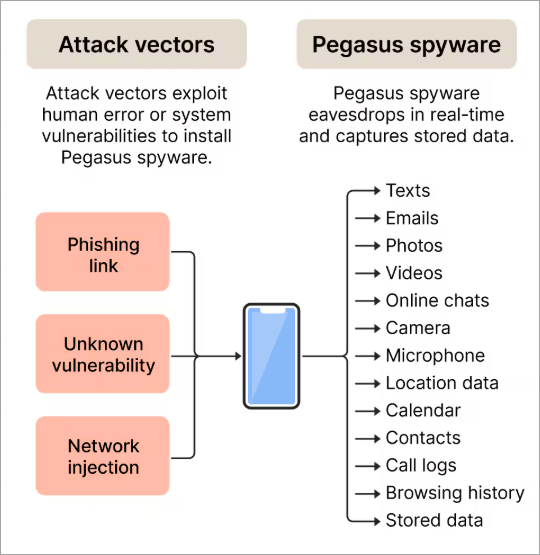
[Via norton.com]
The way it works: Some of the most sophisticated spyware, such as Pegasus, can be used in zero-click attacks on iMessage, WhatsApp, or MMS, so you do not need to touch a single button to be compromised.
How to identify: Consumers make it extremely difficult to detect the problem, but the symptoms include overheating, random restarts, and unusual data consumption. A forensic investigation can reveal such an infection, and security firms can perform such an investigation, such as Citizen Lab and Amnesty International.
5. Phishing and Malicious Links
It works as follows: A user simply has to click on an SMS or email message convincingly created that executes spyware or even provides attackers with privileges that they would otherwise not have.
How to identify: You may be receiving, on your phone, surprisingly frequent requests to add configuration profiles, or you are experiencing frequent browser crashes when you click, or new app icons have appeared.
All of these are red flags that you may experience phishing and malicious attacks. Browsers and security applications can confirm using anti-phishing features.
6. SIM Swapping
The way it works: The way it works: Hackers persuade your mobile carrier to give them a new SIM under your number, and this allows them to intercept your calls and messages, including 2FA codes.
How to tell: Cellular service loss. If you cannot send or receive text messages, or your carrier tells you that your SIM card is activated, you will know you have a hacked phone text message. Contact your carrier and lock your account using a PIN.
7. Malicious Wi-Fi Networks
The technical method hackers use to install rogue Wi-Fi hotspots in cafes, airports, or hotels that intercept all your non-encrypted traffic and occasionally inject malicious settings into your phone.
Detection: When a Wi-Fi network with a recognizable name asks you log in and the action request appears as an odd procedure, or when your phone loses signal constantly, there may be a rogue hotspot. Use a VPN and go through your Wi-fi for suspicious proxy entries. If you are looking for the best VPN, then check our detailed guide on the Top Free VPN for Windows.
8. Hardware Tapping Through Amended Accessories
How it works: How it works: Attackers either use hardware such as chargers, charging cables, Bluetooth dongles, or counterfeit headphones, which may have built-in hardware that contains spyware or logs audio.
Detection: If your phone behaves strangely when being charged, for instance, overheats irregularly or adds some new background tasks or pops up some permission requests in a manner that is unexplained, it may be that the device into which you just plugged the phone has malware. Buy accessories and hardware from trusted brands and monitor system logs on rogue USBs.
9. Cloud Account Compromise
How it works: Hackers can gain access to their synced messages, calls, and backups without ever actually having access to your physical device through the cracking of your Apple ID or Google account.
How to notice: If and/or when you notice odd logins on your account activity log, alerts via emails regarding password changes on your account, or unfamiliar devices that have been utilized to log into your account, there certainly should be cause for alarm. To tackle such issues, turn on 2FA and scan the account access logs frequently.
10. Hackers and Insider McLain
How it works: In infrequent but actual situations, the employees of carriers or service providers utilize their authorized access to eavesdrop or reroute conversations/texts to spy.
How to identify: In case you see suspicious changes in your accounts that are not explained, provisioning changes, or insider alarms, ask your carrier to provide an account log in detail. Next to go to customer-protection departments and, possibly, complain to the FCC.
Technologies to Detect When a Phone is Tapped
This section includes applications and non-application-based technologies to detect when a phone is tapped.
The process of checking for a tap is a combination of software scanning, system-log inspection, carrier-level diagnostics, and professional forensics. Some of the methods are visible to a typical user, and others need a professional.
Apps and scanners (mainstream use): mainstream mobile-security suites (Norton, McAfee, Avast, Kaspersky, Bitdefender) can identify a great deal of known stalkerware signatures, suspicious apps and behaviors, and provide guidance; but they cannot identify all of them, particularly the fairly high level of customized commercial espionage.
Best Tools to Monitor & Avoid Phone Tapping
Here is a list of the top tools to monitor Phone Tapping.
- Norton Mobile Security / Norton 360 (Norton)
- McAfee (McAfee Mobile Security)
- Avast (Avast Mobile Security)
- Kaspersky (Kaspersky Mobile Security)
- Bitdefender (Bitdefender Mobile Security)
#1) Norton Mobile Security / Norton 360 (Norton)
Here is a short overview of how Norton assists in phone tapping detection.
Norton Mobile Security offers protection against malware and stalkerware, application behavior analysis, and privacy-related features (such as permission audits and suspicious battery/data usage notifications) that allow identifying most spyware activities that are commonly used in phone taps.
These safeguards ensure Norton is a robust consumer-level entry-level security in cases where you fear being spied on.
Norton provides step-by-step instructions on how to check whether your phone is tapped.
Step 1: Download Norton Mobile Security (or Norton 360) at the official Play Store or App Store and go through with the initial setup.
Step 2: Conduct a complete device scan on the Norton dashboard (tap Scan / Start scan) to allow Norton to search the apps installed on the machine, the hidden components, and the known signatures of spyware. Wait for the completion of the scanning and then check the findings.
Step 3: Check permissions on the Norton app and the reports on privacy to view apps with high-risk permissions, then flag those apps with permissions that you do not recognize.
Step 4: Check the data-usage or battery-behavior notifications (where they exist) by Norton that could depict a background exfiltration process characteristic of stalkerware. In case Norton reports suspicious behavior, make observations of the app name and the timing.
Step-by-step process to prevent phone tapping with Norton:
Step 1: Should Norton detect a malicious or suspicious application, Quarantine or remove it according to the in-app instructions. Norton normally offers the choice of either removing or quarantining the threat.
Step 2: Revoke high-risk permissions of the violating app (microphone, camera, location) manually in system Settings and remove device-admin permissions of Android apps (where applicable) to uninstall them.
Step 3: Once removed, always reboot the phone and scan again with Norton to ensure that it is clean, update valuable passwords using a clean gadget, and ensure that key accounts have strong 2FA input. In case Norton fails to uninstall an intractable app, save valuable data first, and then do a factory reset and install only reliable apps.
#2) McAfee (McAfee Mobile Security)

Here is a short overview of detecting phone tapping with the help of McAfee.
The mobile product provided by McAfee is a scan of malware, privacy, and insight into app permissions; it can identify normal spyware, suspicious activities (e.g., apps with abnormal permissions or background data usage) that usually go hand in hand with phone tapping. Its Scan and Privacy options are handy, fast checks for consumer users.
Checking whether your phone is tapped with the help of McAfee – a step-by-step process.
Step 1: Install the official McAfee Mobile Security application either in Google Play or the App Store and configure it.
Step 2: Each time you want to do a thorough scan of installed applications and files, tap the main “Scan” or “Start Scan” of the app; look at the results and find out any detected spyware or suspicious applications.
Step 3: Scans the privacy and permissions settings (McAfee has) to see the list of apps with access to the mic/camera/location; look at the applications with high privileges or suspicious names. Check battery consumption and the usage of data.
Stopping it with McAfee, follow these steps:
Step 1: In case the scan detects malware or stalkerware, remove it using the quarantine/removal instructions provided by McAfee (removal). McAfee normally provides a one-tap cleanup flow on flagged threats.
Step 2: Revoke any dangerous permissions and strip any suspicious Android application of device-admin privileges manually, to uninstall it, and in case of failure, boot into safe mode and uninstall it manually.
Step 3: Once remedied, perform another scan with McAfee, restart the device, change passwords with an alternate device, and watch out for any suspicious activity. If the compromise is so severe, save valuable files and perform a factory reset.
#3) Avast (Avast Mobile Security)
The Avast Mobile Security also includes a feature called Smart Scan that scans for malware, suspicious applications, problematic settings, and suspicious application behavior; its anti-spyware recommendations help identify stalkerware and applications seeking intrusive permissions usually used to tap phones. Avast has easy-to-follow removal instructions.
Using Avast to check if your phone is tapped, step-by-step.
Step 1: Install Avast Mobile Security from the Play Store or App Store, open it, and run the first Smart Scan, which will identify malware and dangerous applications.
Step 2: Open the Privacy or App Status sections to view which applications have permission to use the microphone, camera, or location, and take note of any applications that seem strange or other applications with strange names.
Step 3: When Avast identifies a suspicious application as stalkerware or malware, the detailed detection report (app name, path, permissions) should be reviewed, and the device’s strict administrator or access permissions should be recorded.
How to stop it with Avast – step-by-step.
Step 1: Click the option of Removal or Uninstall recommended by Avast under the threat: repeat the prompts to remove the application and other related elements.
Step 2: In case you cannot delete the app, navigate to the Settings app on your Android, then under Device Admin apps, revoke permissions, or uninstall using Safe Mode; on iOS, delete suspicious profiles and reset network/settings.
Step 3: After removing, restart the phone, run Avast Smart Scan, just to ensure that everything is clean, change the passwords on your account, and enable stricter app permission hygiene in the future. Reformat in case of persistence of behavior.
#4) Kaspersky (Kaspersky Mobile Security)
Kaspersky Mobile Security provides explicit stalkerware detection as one of its scans, and specifically promises to identify stalkerware during quick or full scans; it also provides permission auditing and network-activity monitoring to identify suspicious data escaping the system.
Kaspersky has issued specific advice and utility (such as TinyCheck) on how to identify the presence of covert surveillance.
Kaspersky’s method for detecting phone tapping is explained below:
Step 1: Install Kaspersky Mobile Security from the official store, open the application, and proceed to install and update the databases on viruses. Kaspersky will focus on the latest definitions of stalkerware.
Step 2: Full/Quick scan – the Stalkerware Detection unit of the Kaspersky software must identify any known monitoring programs, and may include information about suspicious programs.
Step 3: Check passive network indicators and permissions to applications with the help of Kaspersky privacy tools and TinyCheck advice (Kaspersky has published techniques and research on network-side detection) to evaluate these indicators and permissions.
How to prevent it with the help of Kaspersky – step-by-step.
Step 1: On detection of stalkerware, Kaspersky will recommend removal/quarantine; otherwise, it will provide a list of the problematic files or applications in the app to allow you to follow the directions.
Step 2: Unless the permission is dangerous, delete it, delete device-admin rights, delete the offending app, and reboot. If the app is robust, then use Safe Mode uninstall or factory reset after saving valuable information.
Step 3: Once cleaned, scan again with Kaspersky to ensure it has been removed, and you might want to perform the Kaspersky TinyCheck procedure or some other network-monitoring procedures in case you suspect a sophisticated remote control. Reset all the account credentials in a secure device.
#5) Bitdefender (Bitdefender Mobile Security)
Bitdefender Mobile Security is a malware scanner and privacy advisor with the ability to scan the apps’ access permissions and tips on identifying invasive or unnecessary app access. Its user tutorials and blogs provide information on how to detect and delete invasive spying apps.
Checking whether your phone is tapped with the help of Bitdefender: Step-by-step process
Step 1: Install Bitdefender Mobile Security through the official store, open it, and update it with the first update of viruses.
Step 2: Conduct a complete scan of your devices with the primary dashboard of Bitdefender to identify any known spyware or suspicious footprints of applications; are in the Privacy Advisor and application-permission reports.
Step 3: Check for apps that have been flagged, the microphone/camera/location permissions, and note whether they have a device administrator or use accessibility features. Bitdefender guides provide instructions on where to find the settings in Android/iOS.
Step-by-step process of how to stop phone tapping with Bitdefender:
Step 1: Use removal/quarantine of Bitdefender-detected malware; go through its remedial checklist.
Step 2: Deny access, take away device-admin privileges of suspicious applications, and delete them. In case the app is stubborn, it can be uninstalled in Safe Mode or factory-reset (with the important data first copied to a storage device).
Step 3: Reformat Bitdefender to ensure the device is free of viruses, rotate account passwords on an authorized computer, turn on a secure lock screen and highly secure authentication, and look out for it as it returns.
Caveats, workflow (short, important), and recommended practical notes.
- Antivirus Is Not a Guarantee: Antivirus software is the first line, not a guarantee. Consumer mobile anti-virus software such as Norton, McAfee, Avast, Kaspersky, Bitdefender, and others may detect most of the well-known families of spyware, but may not in some cases of commercial-grade surveillance or implanting firmware that has been highly modified. Therefore, forensic help may be of importance in case you suspect a serious intercept.
- Avoid Alerting the Attacker: Be coy in case you are afraid of an abusive actor. Other tracking applications will alert the people who control them whether you have installed antivirus software. Thus, think about the danger of informing an abuser before scanning. Kaspersky’s TinyCheck study highlights non-invasive methods for detecting such cases covertly.
- Clean the Device Safely: In case it is dirty, factory reset using a reliable backup. Save the key information (photos, contacts) to a secure location, and then reformat and install only the applications that are trusted. After cleaning, change all your passwords and use hardware 2FA if/and when available.
- Look Beyond Installed Apps: Look for indicators in the OS-level indicators such as battery graphs, Android permission lists, iOS configuration profiles, iOS device-admin, and Android developer options/ADB logs. Also check for indicators on the carrier usage and provisioning through carrier support, and system diagnostics, e.g., iOS Analytics and Privacy, Android developer options/ADB logs. In the depth cases, gather pictures of the gadget and submit them to an authorized forensic lab.
- Escalate to Professional Forensics: Professional equipment and experts, Commercial forensic suites (operating in labs and with police), and professional mobile forensics organizations may conduct file-system imaging, entropy analysis, and trace network exfiltration, actions that consumer antivirus software is unable to execute. In case you have reason to believe that there is a serious violation, refer to certified individuals.
Here are ten third-party companies and services (free and paid) to help stop phone tapping.

[Via eset.com]
The most recommended apps are Norton, McAfee, Kaspersky, Bitdefender, Malwarebytes, ESET, Clario, Lookout, and Trend Micro. You may want to do your due diligence and find out if there are other apps apart from our recommendations.
To analyze forensic and legal quality, apply accredited boutique companies (search mobile forensics lab near you).
How to Avoid Your Phone Being Tapped
Here are the top tips that will help you in preventing from your phone from being tapped:
- Short-term Containment: Put the phone in airplane mode from the phone settings, turn off the Wi-Fi/Bluetooth, and do not exchange any sensitive conversations with the phone until an evaluation of the situation is complete.
- App Updates: Install updates, get rid of suspicious software, change all passwords on a clean computer, and factory-format in case you believe that a persistent compromise exists.
- Hardware: The hardware to consider is one with excellent vendor updates (iPhones and Google Pixels/flagship Androids have long security updates); do not use old or low-cost hardware that is no longer updated with security fixes. NortonStrong authentication Strict passwords, hardware security key (FIDO2), and trusted 2FA.
- Engage Professionals: When handling sensitive cases that require data to be permanently unrecoverable, the use of specialized “attorney-wipe” services or certified digital forensics professionals is recommended.
- Never click on links in SMS, and do not install apps that you are not sure of.
- Deny any app permission requests for unwarranted cases, including permissions to request mic, camera, and location access.
- Avoid using community charging ports to charge your devices.
- Ensure to use company-approved MDM only on work devices and be familiar with the policies set by your employer.
- Turn on the Find My and watch lists. Select a carrier account PIN and report any suspicious activity to the carrier.
- Turn off location sharing and access background apps occasionally.
- Look at hardware tokens for the most sensitive accounts
- Consult security experts for advice on hardened equipment and operational security, in case you are operating in a high-risk environment.
Why and Who May Be Tapping Your Phone? (Legal in the U.S.)
Get to know who may be tapping your phone and why they should do so from this section:
1. Criminals & Stalkers
Opportunistic thieves, abusive partners, or stalkers install stalkerware to spy on the victims and their messages and location. This is illegal in most states and is often prosecuted when the stalkerware is discovered.
To verify, conserve evidence, and turn to the police. Civil protective orders and criminal complaints are some potential solutions.
2. Employers/IT Admins
The use of Mobile Device Management (MDM) by employers on corporate phones to monitor them is legal, given that it is disclosed on company-owned phones; however, it should be used under employment and privacy laws.
Verify by checking on MDM/profiles and enquiring HR or legal advice, whether you feel it is more appropriate to monitor than disclose.
3. Professional Investigators & Commercial Providers
There is an industry of selling tools of lawful interception to their customers. Some buyers use them improperly; in the U.S., any interception without a lawful court order is forbidden under Title III and 18 U.S. C. SS2511. In case of suspicion, take evidence and complain to the police, and may also take legal action.
4. Government & Law Enforcement
Is my phone tapped by the government? An agent may be allowed by law to intercept communications but only under strict statutory procedures (Title III, ECPA) and only following a judicial order, and any intercepts are controlled, and any authorized intercepts are followed/preceded by warrants and legal filings.
In case you believe you are being illegally surveilled by the government, get a lawyer with experience in national-security privacy or civil rights law. So, is my phone tapped by the government? With recent revelations about phone tapping, it is known to many that carrier networks do share information and allow such infiltration.
In both above categories, establishing an intercept may often involve a forensic image, cooperation by the carrier (they may confirm network-level forwarding or provisioning), and legal advice; solutions can be as simple as criminal action or as complex as civil lawsuits, regulatory agency action, and recouping of the account.
Penalties (Under U.S Law) for Phone Tapping
The issue of privacy (tapping of phones) and penalties (under U.S. law) is briefed here.
- Phone tapping is a profound abuse of privacy. It stifles speech and may impose emotional and financial damage.
- Title III and the Electronic Communications Privacy Act criminalize and provide civil redress to persons whose communications have been intercepted, disclosed, or otherwise used without permission and impose considerable penalties on violators. The manuals with the DOJ explain the scope and penalties for violations.
- Another tier is state laws: numerous states consider nonconsent recording and stalking through devices distinct offenses and punishable by their own laws, and a victim can also claim damages in court. In case you suspect illegal tapping, leave evidence and call the police and an attorney; these laws defend you.
How People are Vulnerable to Phone Tapping
The way populations become vulnerable to phone tapping (technology, law, telcos) is explained below.
Technological exposures: many consumers are prone to ubiquitous app stores, unsecured open Wi-Fi, social engineering, and low-cost commercial spyware.
There is a patchwork of state and federal law that may regulate who has access to monitor, and the aggressive practice of data retention/practice at telcos is sometimes combined with the opportunity to abuse it, should provisioning or credentials be stolen.
Along with their responsibilities, telcos and service providers also have access to technical access – carriers may, with legal procedure, offer assistive access; poor internal controls may lead to inappropriate exposure. Consumers are advised to demand transparency from providers, account PINs, billing, and provisioning.
Are There Any Advantages of Phone Tapping
This section explains the attitude of Telco and the service provider on whether there are any advantages of Phone Tapping.
Pros offered by law enforcement:
Title III and ECPA make a distinction that facilitates judicial procedures in the process of carefully supervised taps; targeted intercepts (with warrants) will prevent terrorism, large-scale conspiracies of crime, and child-exploitation rings.
Giving consent to lawful process may also be appropriate, as it is legally required of providers and can be used to ensure the safety of the community.
However, a wide-ranging collection, mission creep, or weak provider management leads to severe damage to privacy and civil liberties.
Telcos publicly focus on legal compliance, transparency reports, and legal process; advocates for privacy usually push for harder limits to be imposed and regulation. It is intricate, heart-wrenching, and the root of contemporary civil liberties.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it possible to have my phone tapped without malware?
Without device malware, carrier-level provisioning, or social engineering, it can intercept calls made using call forwarding. Confirm with your carrier.
2. Is a factory reset a certain way of removing spyware?
In most cases, a factory reset will remove any consumer-grade spyware. However, it may not be aware of advanced implants or firmware-level attacks. Thus, it is best to be certain with a forensic verification.
3. Can the police tap into my phone without a warrant?
Generally, police must not tap into a call without a warrant. Title III of the federal law mandates judicial approval of intercepts except in rare cases of emergencies and exigent situations.
4. Can iPhones resist tapping?
Operating systems are resistant to everything. iOS is more secure and closed, and difficult to hack, having no physical access or a zero-day exploit, but there are still risks.
5. What is the first thing I need to do in case I suspect tapping?
The first thing to do when you suspect phone tapping or call tapping is to save valuable information, switch off or enable airplane mode, report abnormalities, and report to a security expert and a law enforcement agent when necessary.
6. Can carriers detect taps?
Carriers can identify network-level forwarding or provisioning changes, which might help determine suspicious network traffic when you dial them.
7. Do antivirus software detect stalkerware?
A lot of stalkerwares can be identified through the current antivirus software; certain commercial or customized programs do not have the ability to be detected. Apply certified scanners and specialists.
8. Should the compromised SIM be changed?
Changing the SIM in case you suspect it has been compromised, and telling your carrier to reset provisioning and account PIN may be a good step, especially when you are suspicious of SIM-based attacks.
9. What if the phone shows a green/orange dot on iOS?
That green or orange dot on iOS indicates mic/camera use; if you didn’t initiate that use, inspect app permissions and remove suspicious apps.
10. When should I hire a forensic lab?
You may hire a forensic lab for your phone when you suspect tapping and if sensitive evidence exists (recordings, strange logs), if legal action may follow, or if basic remediation fails. A forensic lab preserves evidence and gives authoritative confirmation.
11. Can someone tap my phone without touching it?
Remotely, and in a few ways, such as malicious apps or spyware you install by accident, “zero-click” exploits that require no interaction, or lawful carrier/IMS interception, it may be possible for someone to tap your phone without touching it.
But remote tapping that’s truly stealthy is relatively rare and usually targeted.
12. How long does phone tapping last?
Phone tapping lasts as long as the attacker maintains access, from minutes to permanently, until the spyware/connection is removed or the lawful wiretap order expires. Some infections survive factory resets only in rare, sophisticated cases.
13. Can a factory reset be traced?
A factory reset clears most user-level evidence on the device but does not remove server/carrier records (call/SMS/CDR), nor does it guarantee removal of advanced firmware-level implants. Forensic traces of prior compromise can still often be recovered by specialists.
14. Do phone-tapping apps show up in the App Store?
Legitimate app stores (Apple App Store, Google Play) prohibit stealth spyware, so stealth tapping apps are normally not listed.
However, some legitimate parental-control apps or device-management apps can be misused and may be visible. They may be sideloaded or hidden in Android after installation. On iOS, attackers typically use targeted distribution or exploit chains.
Conclusion
You can avoid call or phone tapping by factory resetting or updating your OS to remove any malicious apps / stalkerware. For cases where phone tapping occurs because of carrier provisioning or call-forwarding abuse, avoid it by locking your carrier account with a PIN, monitoring call-forwarding, and contacting the carrier about anomalies.
To avoid cases of SIM swap/account takeover, avoid them by securing your carrier account, using strong authentication, and alerting the carrier to suspicious port attempts. Where jailbreak/root + firmware tampering may achieve call or phone tapping, avoid it by not rooting/jailbreaking, keeping devices current, and preferring vendors with robust updates.
Network-level lawful intercepts may also occur if you are experiencing phone tapping, which you can avoid being surprised by by understanding legal processes, using end-to-end encrypted apps for sensitive conversations, and knowing your legal remedies if you suspect overreach.
Research Process:
The total time involved to complete and publish this article is approximately 39 hours. The content in this guide was created through a structured research approach to ensure accuracy and reliability.
For more quick phone security guides, you can explore our range of tutorials below:
- Top 10 Mobile APP Security Testing Tools
- The Top 10 FREE Antivirus for Android [SECURE Apps]
- Mobile App Security Testing Guidelines – Software Testing Help
- How To Remove Malware From Android Phone [7 Easy Methods]
- Droidkit Review: Unlock Your Android Phone Without Data Loss
- How to Stop Someone From Accessing Your Phone Remotely







