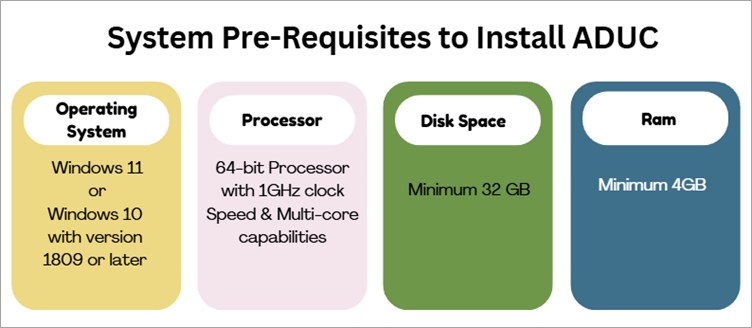
Discover how to install Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) on Windows 11. Manage Active Directory objects like users & groups with simple tips for efficient ADUC management:
Administrators use a graphical interface to create, update, and delete objects within Active Directory, such as organizational units, users, computers, and groups.
This interface acts as an add-on for extending Microsoft management console functionality, widely known as ADUC, which is mainly used for managing Active Directory environments for Windows Server. ADUC is Active Directory Users and Computers.
Table of Contents:
- Active Directory Users and Computers: Installation Guide
- What is ADUC Used For?
- What are Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)?
- How to Install Active Directory Users and Computers on Windows
- Advantages of ADUC
- Tips for Efficient ADUC Management
- Troubleshooting RSAT & ADUC Installation Issues
- Integration of Cloud Services with ADUC
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Active Directory Users and Computers: Installation Guide

Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) is a part of RSAT – Remote Server Administration Tools.
What is ADUC Used For?
Various ADUC functions are:
- Manage, create, update, and delete user accounts, configure access permissions and passwords for these user accounts, and other attributes.
- Create, update, and delete computer accounts, group policy configurations, and computer mapping to the domain.
- Manage groups and facilitate easy access control by assigning users to groups.
- Easy delegation, management, organizing groups, computers, and users in logical units.
- Active Directory objects attribute updates, like contact details like mobile number, email address, etc.
- Moving FSMO – flexible single master operations roles in Active Directory is crucial to prevent conflicts and manage the directory.
- There are five FSMO roles such as:
- Infrastructure Master
- RID Master
- PDC Emulator
- Schema Master
- Domain Naming Master
- There are five FSMO roles such as:
- Control delegation, like assigning/granting permission for administrative tasks to other groups or users.
- With ADUC, administrators can utilise advanced features like:
- NTDS Quotas
- LostAndFound container
- System information
- Program Data
- Create and manage external devices like printers.
What are Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)?
RSAT stands for Remote Server Administration Tools, used by system administrators to manage features and roles in Windows Server remotely via a computer equipped with Windows 7 Service Pack 1 and Windows 10 operating system.
RSAT for Windows 10 platform and tools support matrix says that Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) tools from
Remote Server Administration Tools technology comprises:
- Active Directory Administrative Centre
- Active Directory Sites and Services
- Active Directory module for Windows PowerShell
- ADSI Edit
- Active Directory Users and Computers
You can install the Remote Server Administration Tool (RSAT) in the enterprise edition and not in the home or standard edition of the Windows operating system.
Functions of RSAT
Remote Server Administration Tool (RSAT) is responsible for cleaning Active Directory and ADUC utilised by administrators to remotely manage Active Directory and Windows servers. Administrators can install RSAT on a Windows client by remotely accessing the server.
Various functionalities offered by RSAT are explained below:
- Administrators can remotely manage servers without any need for physical access.
- Consists of various tools such as DNS manager, DHCP manager, Group Policy Management, and ADUC.
- Active Directory administration tasks can be remotely performed by administrators using RSAT.
- Administrators can manage different versions of Windows servers as RSAT is compatible with these server environments.
How to Install Active Directory Users and Computers on Windows
Installation for Windows 7 & 8
- Download & install the RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tool) package.
- Search for Remote Server Administration Tool on the Microsoft Download Center page
Note – You will notice a 404 page with a message as- download is no longer available for Windows 7 as there will not no security updates and technical support for Windows 7 since 14th January 2020, and users with the Windows 7 operating system will be using their computers may face risk of vulnerabilities related to security.
You can, however, download RSAT for Windows 7 with the SP1 package.
After successfully installing RSAT in Windows 2000 or XP client, you need to manually set up as explained below:
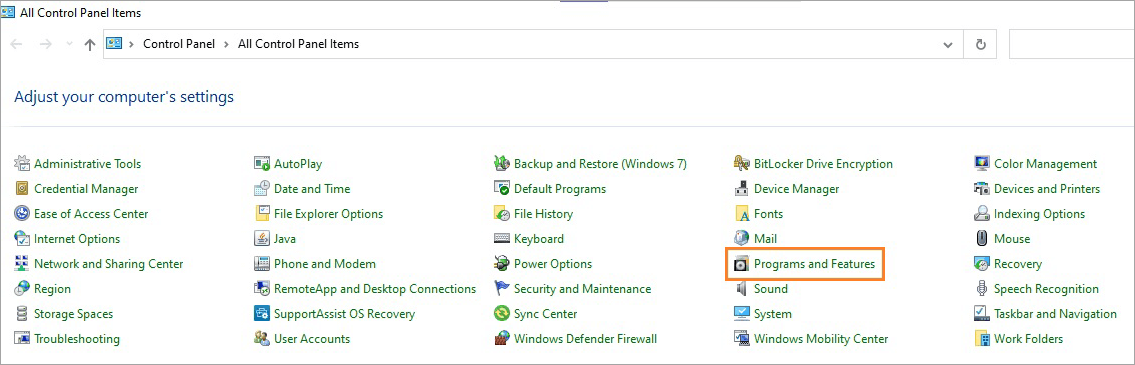
- Click on the Windows (Start) icon
- Search for Control Panel
- Click on Programs and Features from the list
- Click on Turn Windows features on or off.
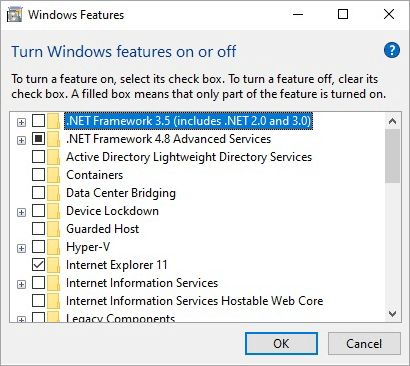
- You can disable or turn off features/tools you don’t need to use a particular tool listed.
- Next step is to enable tools for features and roles to manage the post-installed downloaded package for RSAT in Windows 7.
- Expand RSAT under the Add features wizard & select only those tools you wish to install.
Note: You will require the Enterprise or Pro version of Windows 8.1 to install ADUC (Active Directory Users and Computers) for Windows 8.
Steps to Install on Windows 11
Steps for Installing ADUC (Active Directory users and computers) in Windows 11
- Press Windows icon + R
- Run window will appear
- Type control panel in the text field labelled as Open.
- Press the OK button
- The control panel interface will appear with various icons.
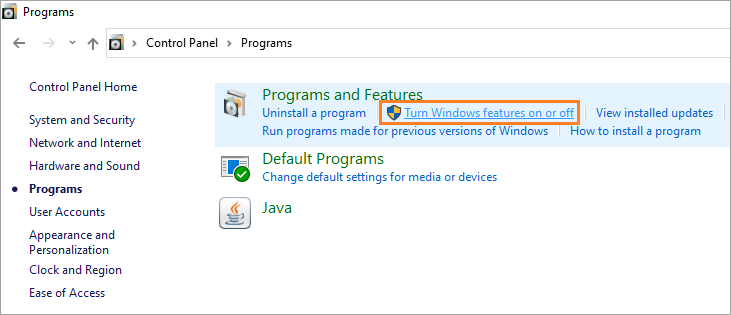
- Click on the Programs icon
- You will find the Programs and Features section on the right pane.
- Click on Turn Windows features on or off
Note: You will need administrator privileges to change the settings.
Search for Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) on a Windows 10 computer:
- Right-click on the Windows icon in the bottom left corner of the screen
- Select Settings from the menu options displayed
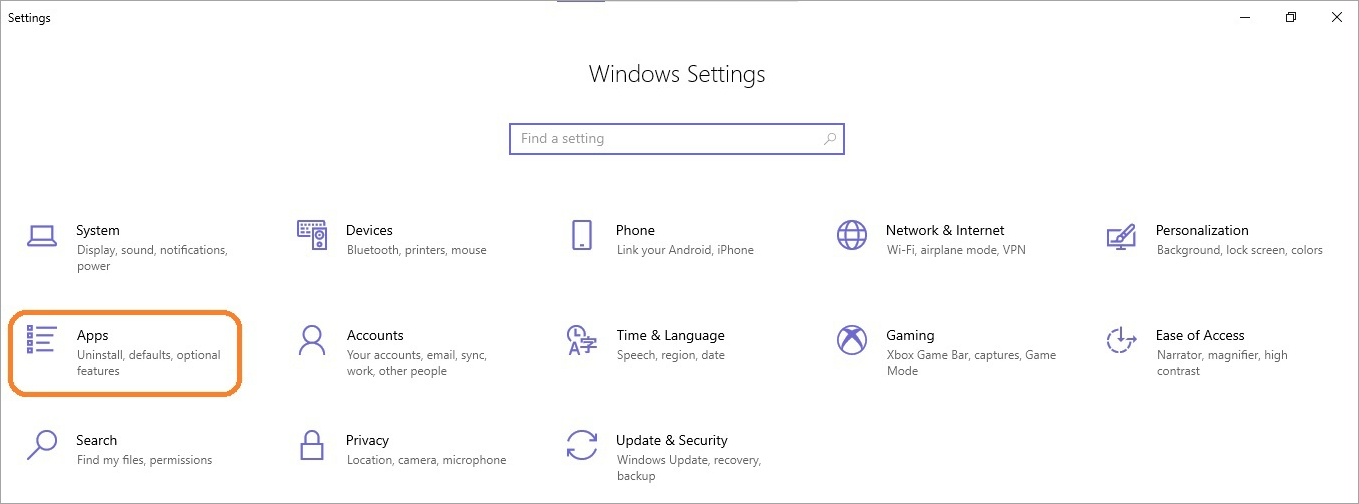
- Click on the Apps icon under Windows Settings
- Under the Apps & features section on the right pane
- Click on the Optional features link
- Click on the + symbol with the label Add a feature
Installation Process on Windows 10
The steps to install ADUC (Active Directory Users and Computers) in Windows 10 will be the same as the steps mentioned above for Windows 11.
Steps to add Active Directory Domain Services & Lightweight Directory Services Tools
Note: If your computer has Windows 10 version 1809, you will follow different steps to install the ADUC (Active Directory Users and Computers) tool. You can install the RSAT tool with the MSI file, else you can access it by clicking Windows Settings optional features.
If your computer has Windows 11 installed or has a newer version than version 1809, you can install going over the internet.
Steps to install ADUC on Computers with Windows 10 version 1809 & above:
The steps include:
- Click on the Windows 10 icon & select the Settings icon from the menus.
- Under Settings, the Windows Settings interface will appear.
- Click on Apps.
- The apps & features user interface will appear.
- Select the Optional features link under Apps & features on the right pane.
- The optional feature will appear.
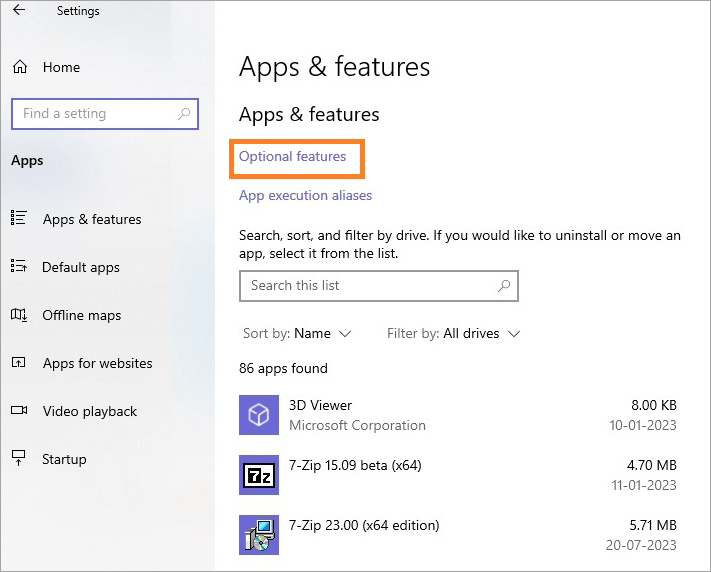
- Click on the Add a feature link with the + sign.
- A window will open with a text field with the label – Add an optional feature.
- Type RSAT, press the search icon
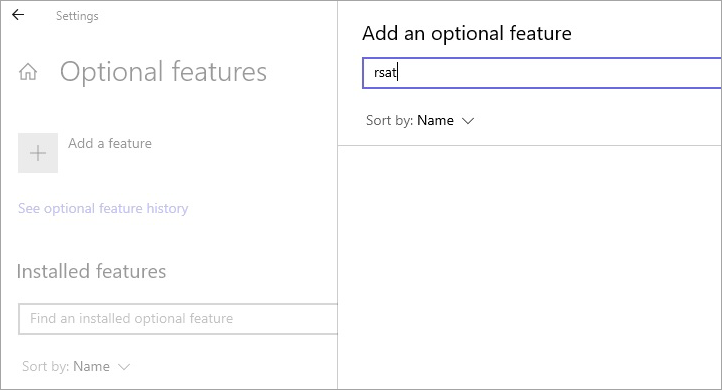
- You will get various search results below.
- Select the checkbox against the search result RSAT: Active Directory Domain Services & Lightweight Directory Services Tools.
- Click on the Install button
- The installation process will begin by downloading the selected tool on your computer.
After successful installation, you can find the software in the menu list.
Install on Windows 8 & Windows 10 Version 1803 and Below
Enlisted below are the steps:
- Search on internet to download Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows.
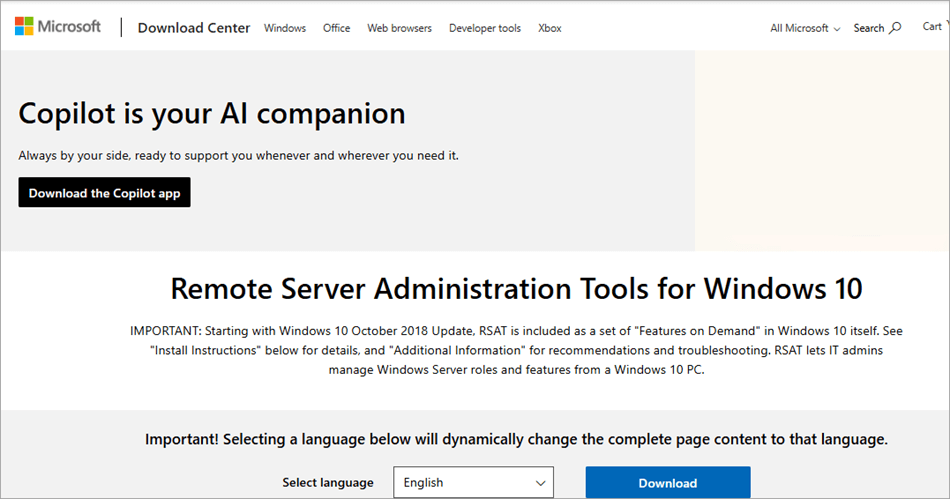
After successfully downloading, look for ‘WindowsTH-KB[7digitNumber]-x64.msu’, double click to install the RSAT tool software.
Once installation is complete, you can view the tool under the start menu when the Windows icon is clicked
There are multiple ways to launch the RSAT tool, as given below.
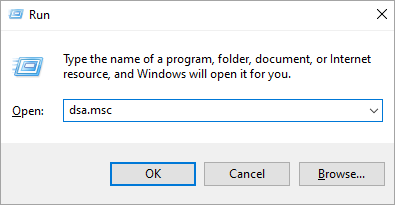
How to Launch the RSAT Tool Using Run Windows
- Press Windows icon + R to open the Run window
- Enter dsa.msc command in the text field provided and press the OK button
How to launch ADUC using the Start Menu
- Click on the Windows icon (Start) in the bottom left corner of the screen
- Look for the Windows Administrative Tools folder
- You will find Active Directory Users and Computers
- Click on it to open the tool
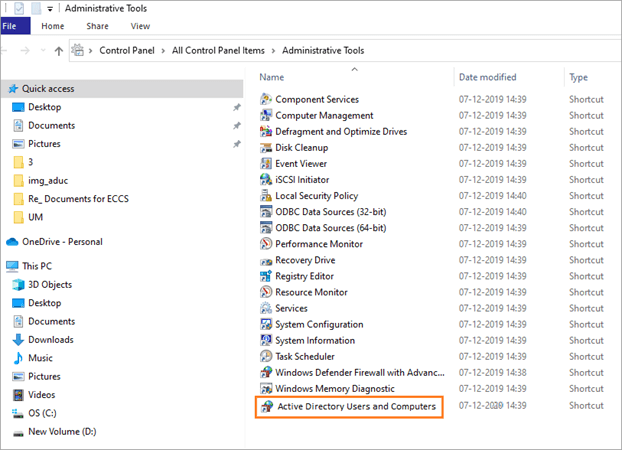
Launch the ADUC using the Control Panel
- Click on the Windows icon
- Type control panel in the search text box
- Select the Administrative Tools icon
Using PowerShell to Check RSAT Tools Installed
Click on the Windows icon (Start) in the bottom left of the screen.
Search for Windows PowerShell in the menu.
Once the PowerShell command prompt is opened, you can type the following command to check which RSAT tools have already been installed on your computer.

Advantages of ADUC
- Single centralized operations for administrators to manage network resources, user accounts, and computers.
- Provision of configuration of security policies for authentication protocol, password requirements, and access permissions.
- Management of user accounts, access rights, and permissions all from a single user interface.
- Administrators can manage access permissions to different user groups for network resources like applications, printers, and files.
- System events and user activities are captured in detailed logs to diagnose and resolve any network-related issues.
- Users can access multiple resources and applications over the network via authentication with a single credentials.
- Scalable as per user base and resources, and can be easily integrated with other Microsoft services like OneDrive, SharePoint, and Exchange for users.
- Administrators can create and apply Group Policy Objects (GPOs) that control the behaviour of users and computers over the network, configure user settings, and enforce security policies.
- Administrators can automate repetitive tasks like group management and user provisioning.
After successfully installing the Active Directory Users and Computers tool, you can do the following:
- Create a user account for Active Directory
- Enable the newly created Active Directory user account
- Disable the newly created Active Directory user account
- Reset password for Active Directory user account
- Delete and remove the active directory user account
- Create an Active Directory group
- Add a new member to the Active Directory group
- Delete the Active Directory group
- Create a new active directory computer account
- Reset the computer account
- Delete the computer account
- Create a new organizational Unit
- Delete the organizational Unit
Here is a video on the Overview of Managing AD with the ADUC Management Console:
Tips for Efficient ADUC Management
1. Access and authorization to resources are done with a single login credential for centrally controlled Active Directory on cloud or on-premises applications.
2. The change control process for Active Directory and group policy needs the following changes to prevent any downtime.
- Nominate a responsible person for change
- Explain the details of the change
- Time and duration of implementing a change
- Impact expected due to the change
- Testing of changes
- Follow backup procedures
3. Group policy tips are as listed below.
- Keep the default domain policy without modifying
- Keep group policy objects at the domain level
- Use a superior quality of OU structure
- Keep the default domain controller policy without modifying
- Apply group policy at the root level of the OU
4. Active Directory is critical to authenticate user resources like email, files, remote access, printers, etc. It is essential to document details of Active Directory, such as Domain Name, NetBIOS name, global catalogue servers, FSMO role holders, diagram of topology and group policy objects, and description about their functionality.
5. Accurately configure domain time by setting the PDC emulator to the source of time and disabling synchronization of time between guest operating systems and the host system.
6. Using a restrictive group to prevent the local group.
7. Using least privilege service accounts.
8. It is necessary to understand the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory service, with details on the domain name, user account (with read access to Active Directory), and the OU that has the user present and distinguished name path.
9. Automation of common active directory tasks like creation, Modification, and Removal of user accounts, managing group membership, clean-up of Active Directory (AD), clean-up of file copies and directory, Software deployment, Inventory, and Decommission of assets like Windows and 3rd party patches.
10. Keep track of changes in logging and events in Active Directory for events like
- Deletion of file(s)/folder(s)
- Changes in Group Policy
- Updates to account privileges
- Changes to objects,
- Failed logon attempts,
- Successful logons
11. Configuration of permissions for non-admin helpdesk using the delegation control wizard.
12. Adding descriptions to Active Directory objects.
13. At least once a month, keep cleaning up Active Directory.
14. Apply resource permissions using security groups
15. Checking Active Directory (AD) health using commands like dcdiag to verify domain controllers, test domain naming services (DNS), repadmin command to test replication.
16. Whenever possible, try using Core Servers like domain controllers, DNS, and DHCP.
17. Monitoring of Active Directory having premium tools.
18. Good naming conventions like Users, Groups, Computers, Servers, and other AD Objects for a Standardized Naming Convention.
19. Following best practices for Active Directory OU structure.
Troubleshooting RSAT & ADUC Installation Issues
While installing remote server administration tools and Active Directory Users and Computers – RSAT and ADUC, respectively, it is mandatory to verify firewall restrictions, group policy settings, and check if the correct version of RSAT has been installed or not. In case ADUC does not start, check for configuration for TCP/IP filtering and verify port 389.
Given below are the troubleshooting steps for installing RSAT and ADUC:
- Verify firewall is enabled and Windows Update is used by RSAT
- Make sure you have installed the correct version of RSAT compatible with your operating system
- Validate configuration settings for group policy in case you are on a domain.
- Specify settings for optional component installation, and the component repair policy should be enabled
- Download repair content and optional features are checked directly from Windows Updates
- Ensure the ADUC shortcut is pointed to %SystemRoot%\system32\dsa.msc by right-clicking on ADUC listed in the start menu, else uninstall and reinstall RSAT.
- In case ADUC does not start, check if TCP/IP filtering is properly configured and port 389 is not blocked
- In case you come across error code 0x800f0922 (CBS_E_INSTALLERS_FAILED), try to clear the Windows temporary folder at location C:\Windows\Temp
- Try to install RSAT using the PowerShell command – Install-Windows Feature.
- If you face trouble in installing RSAT on the domain-joined machine, disconnect the machine from the domain & try installing RSAT and then reconnect/join the domain again.
- You can find logs for reviewing/analyzing error messages at the following folder locations
- C:\Windows\logs\cbs
- C:\Windows\logs\dism
- Try to use feature on demand – RSAT FOD or download an ISO image and locally install RSAT components in case you face issues while installing RSAT.
Further Reading => Top Password Managers to Look For
Integration of Cloud Services with ADUC
Integrating Active Directory with Cloud services like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, or Amazon Web Services has multiple advantages
- Consistency between On-premise and Cloud resources
- Central management of user authentication, authorization, and identities
- Combined user experience as it takes the same access permission and credentials to connect both on-premises and cloud services.
- Configurable permissions and access policies at the Active Directory level, and the same applies to cloud services for uniform access management.
- Single Sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) will provide security and streamline user authentication.
- As there is no need to configure separate credential management for on-premises and cloud services, this will save cost.
Enhancing Security in AD Management for Windows 11
It is essential to protect and secure the management of Active Directory for Windows 11, by implementing strong password-related policies, using features like Azure AD Connect and Credential Guard.
We can enhance security protection by utilizing features of Azure Active Directory for access management and cloud identity, like Windows Hello for Business, to secure authentication.
Following general security practices like granting bare minimum access to each account, securing administrative hosts for active directory management, host-based firewalls, and enabling LDAP signing to protect against vulnerability and attacks.
Further Reading => Best Vulnerability Scanners
Videos for Installation of RSAT
Install Active Directory Users and Computers In Windows 10
How to Install Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) + RSAT tools on Windows 10
Videos for creating, deleting, and modifying AD user accounts
Managing Active Directory User Accounts
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are remote server administrative tools?
Remote server administrative tools (RSAT) help administrators remotely, without connecting directly to a server, manage roles and features of Windows Server, and manage multiple servers instead of connecting each of these servers separately.
2. What does RSAT for Windows 10 contain?
RSAT for Windows 10 has components like PowerShell cmdlets, command line tools, server manager, and Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-ins.
3. How to verify that RSAT is installed?
Open a command line application like Windows PowerShell and type the following command & press the Enter key
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Select-Object -Property DisplayName, State
It will display a list of RSAT tools and their status – installed or not installed
4. How do administrators use Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC)?
Administrators use a graphical interface to create, update, and delete objects within Active Directory, such as organizational units, users, computers, and groups. This interface acts as an add-on for extending Microsoft management console functionality, widely known as ADUC, which is mainly used for managing Active Directory environments for Windows Server.
5. Where can you download RSAT (Remote Server Administrative Tool)?
You can download RSAT for Windows 10 from https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=45520
6. What is ADUC?
ADUC is a graphical interface to create, update, and delete objects within Active Directory, such as organizational units, users, computers, and groups.
Conclusion
Active Directory Users and Computers is part of the remote server administration tool and is essential for extending the functionality of the Microsoft management console, used to create, update, and delete objects within organizational groups, units, computers, and users, widely known as Active Directory.
We have explained AD DS and AD LDS tools from RSAT, offerings of ADUC features, Benefits of ADUC, and the importance of RSAT. We further described the installation procedure for different Windows versions.
Tips for efficient ADUC management and troubleshooting RSAT and ADUC installation issues are discussed in this article. Finally, we discussed the frequently asked queries related to ADUC.







