A complete Step-by-step guide on how to delete user profiles in Windows 10 or 11. Quickly remove user profiles in Windows and explore the various ways to delete the user profile registry from this article:
Windows user profiles are a unique feature that allows users to configure personal preferences, files, and settings and separately identify themselves from other users using the same device.
It helps system administrators locate a particular user among multiple users using one computer, allowing registered users limited access to files and system resources and protecting devices from unauthorized modifications and access.
Table of Contents:
- Remove User Profile in Windows 10: Simple Guide
- Types of User Profiles
- Reasons For Deleting a User Profile
- Quick Steps: How to Delete User Profiles in Windows 10 & 11
- Steps to Remove a User Profile in Windows 11
- Registry Editor
- Using File Explorer
- Using Windows PowerShell (Admin)
- Using Group Policy to Manage User Profiles
- Prerequisites for Server Manager Dashboard
- How to Delete User Profiles in Windows 10
- FAQs on Windows User Profile Deletion
- Conclusion
Remove User Profile in Windows 10: Simple Guide
Types of User Profiles
There are four types of user profiles: local, roaming, mandatory, and temporary.
Local: This profile gets created and stored in the hard drive of computer when the user logs on to the system for the very first time. Any changes to the local profile will be specific to a particular computer where changes are saved and for the user who logged in for the first time.
Roaming: Exactly the same as that of a local user profile, and gets copied, and saved to the server in the network, allowing the user to access all the network computers connected to the server where the profile is copied and stored.
Mandatory: The System administrator can access and make modifications if any. Once the user logs off the computer, the configuration changes they made to the desktop will be lost.
Temporary: These profiles are short-lived. At the end of the session, the system will delete changes to desktop settings and create profiles. Windows 2000 and later editions include temporary profiles.
These store user-specific configurations but differ in how they handle changes and their locations of storage. Local user profiles are locally stored, and roaming-type user profiles are synchronized and stored on the server. Mandatory user profiles are read-only and are roaming user profiles.
When the local user profile is deleted, all data and files of the user account and the content of the profile folder are removed. When you delete the user profile of the user who has a roaming user profile, the server copy of his profile is unaffected, but the copy of his local cache profile will be deleted.
Reasons For Deleting a User Profile
There are multiple reasons for deleting the user profile
#1) Troubleshooting Profile Issue: You will have to reset data and settings or configuration the user has done to find and resolve issues related to missing or corrupt profile-related settings, information, or settings made by the user or have synchronized applications with the profile.
It is important to isolate an issue while troubleshooting. Therefore, delete the user profile; then, after identifying and resolving the issue, create a fresh new profile.
Also Read => Extensive Study of Network Troubleshooting with the Tools used
#2) Start Fresh: Corporates assign devices to their employees so that they can deliver their tasks after hours or weekends or remain available for 24/7 critical support. While employees resign, system administrators delete the existing user profile, or e-commerce companies delete the user profile of returned laptops and sell them as open-box items at lower prices.
#3) Block Access: Deleting the user profile will prevent the user access to the device as the user will no longer access the device. It also removes all email accounts, personal settings, configurations, and preferences for applications and personal folders associated with the profile.
Quick Steps: How to Delete User Profiles in Windows 10 & 11
| Method | Steps |
|---|---|
| Control Panel | Control Panel-> Security & Maintenance -> System -> Advance System Settings -> Advance Tab -> User Profile -> Settings -> Select User from list -> Click Delete |
| Registry Editor | Type Registry Editor in Search option -> Go to “Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion \ProfileList” Look for User profile folder -> Remove ProfileImagePath value |
| File Explorer | Press Windows icon + E keys together. File Explorer will open Click on C:/Users You can delete particular user by right click & select Delete to remove the user profile. |
Steps to Remove a User Profile in Windows 11
There are multiple ways you can delete user profile in Windows-based laptops or computers. You will require permission to access configurations and update or delete user profiles in Windows-based devices.
Any of the following steps will require Admin rights to access and continue with further steps.
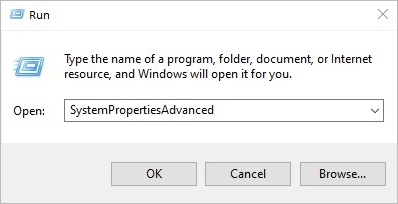
Using SystemPropertiesAdvanced command
- Press the Windows icon + R keys together
- Type SystemPropertiesAdvanced in a search text field on the bottom left corner of your screen.
- Press the Enter button.
OR
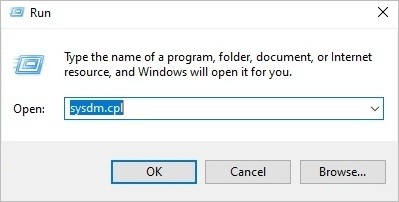
Using sysdm.cpl command
- Right-click on the Windows icon in the bottom left corner of your monitor
- Click on Run from the menu list, and a window with the Run label will open
- Enter sysdm.cpl in the text field provided in the Run window
- Press Enter
OR
Via Control Panel
- Look for the Control Panel icon on your screen
- Click on the Security and Maintenance icon from the list in the Control Panel
- Click on the System icon
- Settings interface will open
- Click on the Advanced system settings link
- System Properties Window will appear
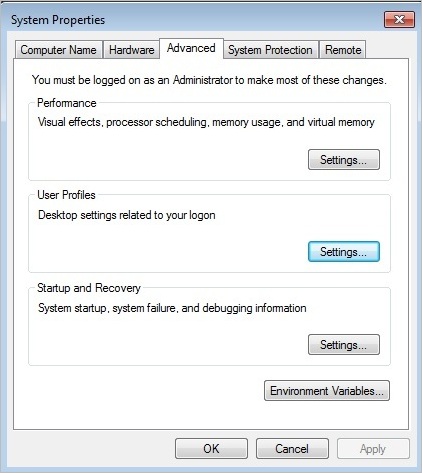
- Click on the Advanced tab
- You will see separate sections such as Performance, User Profiles, and Startup and Recovery with a settings button for each of these.
- Click on the settings button under the User Profile section
- User Profile Window will appear with a list of Users registered for your computer
- You can select a particular user from the list that you want to remove
- Click on the Delete button
- You will get a pop-up window asking to verify your action
- You can click the Cancel button in case you change your mind
- Click on the Delete button, and it will remove/delete the user profile from your computer
Note: Deleting the user profile will remove access permission of the user to the device, delete all the files, his personal configuration setup, download, and data files.
Tips/Precautions:
- The user whose profile is getting deleted should be logged out.
- You will need administrative privileges to delete the user profile.
Registry Editor
You can use the registry editor to delete the user profile on a Windows 10 device in the following steps:
- Right-click on the Windows icon in the bottom left corner of the screen
- Type Registry Editor in the Search option
- Registry Editor will appear
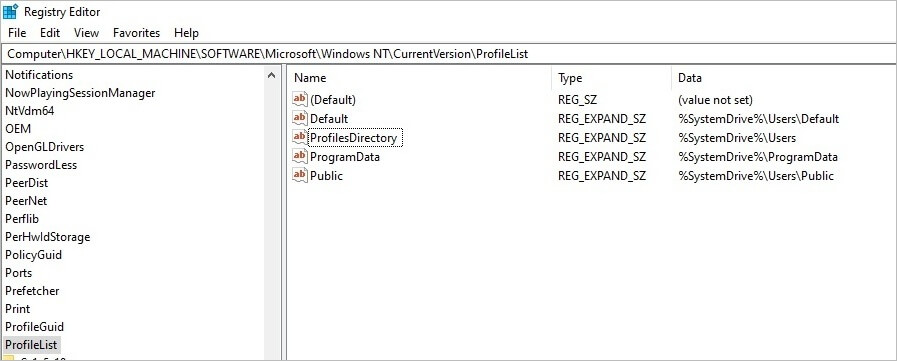
- Go to
- “Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList”
- Look for the User profile folder
- Remove ProfileImagePath value
Also Read => Top Free Registry Cleaner for Windows Systems
Tips/Precautions:
- Take back up of the registry before making any configuration changes.
- The user whose profile are getting deleted should be logged out.
- You will need administrative privileges to delete the user profile.
Using File Explorer
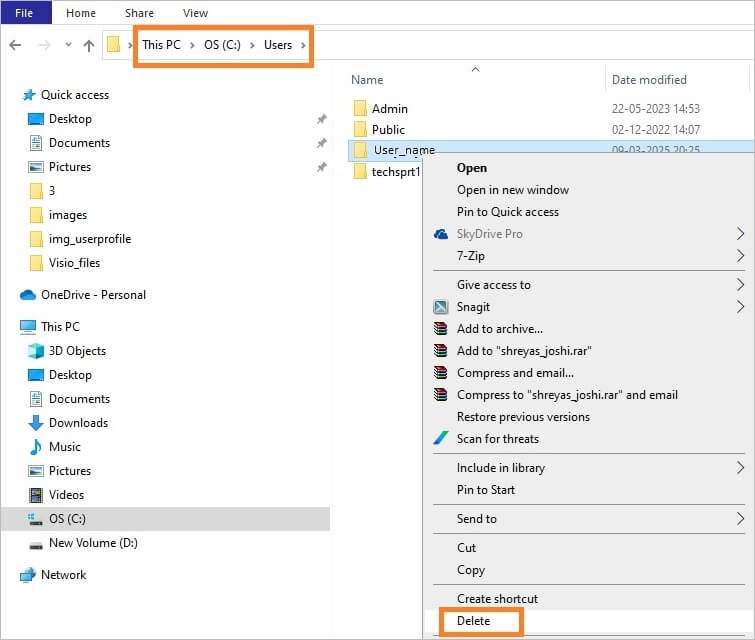
- Press Windows icon + E keys together, OR right-click on the Windows icon & select File Explorer.
- File Explorer will open.
- Click on C:/Users, you will see a list of registered users for the Windows computer.
- You can delete a particular user by right click & select Delete to remove the user profile.
Using Windows PowerShell (Admin)
- Right-click on the Windows icon on the left bottom corner of your screen.
- Select / Click on Windows PowerShell (Admin) from the list.
- Windows PowerShell command prompt will appear.
Ps1 file creation
Type in the following command
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile
This will list domain user profiles on your computer
Append the below command to the above command to list users who have not logged in the given timescale (since 30 days)
Where {(!$.Special) -and ($.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30))}
Remove user profile
Type the following command to remove/delete the profile
Remove-WmiObject
You can use the below command to remove users who have not logged in to the computer for the last 30 days
The entire command, separated by pipe separator |, is given below:
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$.Special) -and ($.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30))} | Remove-WmiObject
This will remove the user profile folder and list of profile entries from the registry.
Tips/Precautions:
- It is recommended to use Delete() or Remove-LocalUser method for deleting user profiles using PowerShell (admin).
- Do not forget to create system restore point prior to deleting user profile.
- Confirm the profile path before running the delete command to avoid deleting the wrong user profile.
- Make sure you do not delete the default user profile, as this may result in a serious system issue.
- Before deleting the roaming user profile, make sure it is synchronized and its backup is taken.
- The user whose profile is getting deleted should be logged out.
- You will need administrative privileges to delete the user profile.
Using Group Policy to Manage User Profiles
Active Directory: A Directory of set of services that facilitate access to resources securely for a networked Windows environment is known as Active Directory.
Further Reading => Ways to Install Active Directory Users and Computer
Active Directory supports user authentication, authorization, and multiple resources throughout the network. Organize a central repository for network resources and devices like servers, printers, computers, and enforce or define security policies across multiple devices and users with the help of Group Policy and storage of information about network objects like printers, computers, user groups, and users in the hierarchical structure.
It supports Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) for services and applications to interact with information retrieved and authentication, Provision of name resolution services by integrating domain name system (DNS).
Group Policy: Administrators utilize it to securely manage devices and users in the Active Directory environment. Four Group policy objects include deployment of software like updates or patches on various machines, configuration for start-up, login and log out, and configuration settings of desktop scripts.
Accessing shared folders, applications, and printers in a networked environment, settings like password and account lockout policies, and configuration for the setting of firewall.
We can create or modify existing group policy for enabling or configuring auto deletion of user profiles that are older than the number of days on the restarting system at the location.
Computer Configuration -> Administrative Template -> System -> User Profiles
You can open, and update the Group Policy as per the steps given below:
- Press the Windows icon +R keys simultaneously
- Run window will appear
- Enter gpedit.msc and hit the Enter key
- Local Group Policy Editor interface will appear
- Look for Computer Configuration
- Select Administrative Templates
- Click on System
- Select User Profiles
- You will check for the policy labelled as “Delete user profiles older than a specified number of days on system restart”,
- You can double-click on this to open policy settings
- Check the enabled option.
- You can enter the number of days in policy settings, like 30 or 90 days
- Click the Apply and OK buttons
- This will save the changes
- You can verify the above changes in group policy by opening the command prompt as administrator, & type command as gpresult/r /scope computer
- Press Enter, and you can see changes in applied group policy object listings
Server Manager Dashboard has some benefits as listed below
- Manage local as well as remote Servers (Windows-based) through a single console – without the need to enable remote desktop protocol (RDP) connections or physical access with each server.
- Dashboard will display a graphical overview of events, performance, and status of the server and updates for managed servers.
- Easy configuration/installation of server features and roles – like DHCP, DNS, IIS Web Server, and Active Directory domain services.
- Add, configure, and remove multiple servers.
- Server performance like memory usage, CPU usage, and disk I/O.
- Viewing Event log entries, configuring service alerts, and performance counters.
- Receiving Notifications and Alerts for issues and events related to the server.
- Violation in best practices, and identifying potential issues in configuration.
Prerequisites for Server Manager Dashboard
Installing Remote Server Administration Tool and Locate Server Manager
Installation of Remote Server Administration Tool – RSAT by accessing Microsoft download webpage URL – https://www.microsoft.com/en-in/download/details.aspx?id=45520 you will find download button as shown below
You can look for Server Manager either at the Start Menu, Search text field, or from the Taskbar, click on Service Manager
Tip: Check if Show administrative tools setting is enabled in Start Menu Settings, – in case the Server Manager tile is not found after RSAT is installed.
How to Delete User Profiles in Windows 10
If you want to delete the user profiles from your Windows 10 PC, then you can follow any of the methods mentioned above. The methods for deleting the user profiles are the same for Windows 10 and Windows 11.
Precautions before deleting Windows user profiles
It is essential and secure to take precautions and check for the following actions before deletion of a user profile on a Windows computer.
- You or a person deleting a user profile must have administrative privileges as mentioned,
- You have taken a backup of important data (files, images, photos, etc.) from the user’s profile, before deleting his/her profile.
- User for which we are deleting profile – should have been logged out, as well as there should not be any programs to continue running listed under user account
- You can take a full system backup OR a restore point so that you can roll back or restore the previous system in case you accidentally deleted some other user instead, or you face the issue and cannot delete a specific user profile.
How To Delete A User Account In Windows 10:
FAQs on Windows User Profile Deletion
1. How many ways you can access Advanced System Settings?
There are multiple ways you can access Advanced System Settings
– Right Click on My PC icon & selecting properties
– From command prompt – SystemPropertiesAdvanced OR sysdm.cpl command
– Open File Explorer & right click on This PC & select properties
2. What will be lost when the user profile is deleted?
When the user profile is deleted, the user will not be able to login again as his login credentials are lost, user data, preferences, or configurations will also get deleted permanently.
3. What is the difference between User profile deletion and user account deletion?
When the user profile is removed from the system, the user’s settings, downloads, data, and preferences get permanently removed, but the user account is still present. When the user account is deleted – the user profile, data, downloads, settings, access permissions, etc. all gets removed.
4. What if the system admin has accidentally deleted my profile, but I still want to login?
If your profile has been removed accidentally, but your account still exists on your computer you can request the system admin to create your profile again allowing you to access your computer.
5. What is the difference between a user with a local user profile and a user with a roaming user profile is deleted?
When local user profile is deleted, all data and files of the user account and contents of the user profile folder get removed. When you delete the user profile of the user that has a roaming user profile, the server copy of his profile is unaffected, but the copy of his local cache profile will be deleted.
6. Where is the user profile registry folder in Windows 10?
The location path of the user profile registry folder in Windows 10 is as shown below
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SOFTWARE/Microsoft/Windows NT/CurrentVersion/ProfileList
7. How do I remove a user from the Windows login screen?
You can follow steps as listed below to delete/remove user from the Windows login page.
Click on the Windows icon –> look for Settings and click on it, Click on the Accounts icon
Look for Family & other users, if found click on Other users, you will find list of users available on your computer.
Right-click on the name of the user you want to delete the profile.
Click the Delete option from the list to delete the selected user profile.
8. What is a User Profile in Windows?
Windows user profile is one of the unique features allowing users to configure personal preferences, files and settings and separately identify from other users using the same device.
Conclusion
User profiles are of four main types – local, roaming, mandatory, and temporary.
In this article we have learned the importance of user profiles, the need to delete user profiles and various ways you can delete user profiles in Windows 10 or 11 computers, along with tips and precautions you should take prior to deleting user profiles.











