Windows Boot Manager is a crucial component responsible for managing the startup process of various Windows operating systems. Follow these simple steps to know how to enable or disable it:
The operating system is the life of every computer; without it, no system can function; it would be like a human without flowing blood. Different computer makers have distinct operating systems that help share and manage resources within the system.
This article will discuss the Windows boot manager that can be used for Windows operating systems.
Windows Boot Manager: How to Troubleshoot

What is Windows Boot Manager
The Windows Boot Manager is also known as Boot Loader. When your system is off, all critical system data, including operating system files, is stored inside your hard drive. So, the Windows boot manager acts as the software that loads the computer’s operating system from the hard drive during the start-up process.
You can have more than one operating system installed on your computer. It is the function of the Windows boot manager to help with your operating system selection and other things. We are going to show you how to configure and reinstall the Windows boot manager and how to fix startup errors on the Windows boot manager.
Importance of Windows Boot Manager
The Windows Boot Manager plays a major role in system operations. It is called a boot loader because it will load the operating system from the Secondary storage (Hard drive) to the Primary storage (Random Access Memory) so that your system can start.
This boot manager can also help to boot your system from a CD/DVD drive, USB drive, or a floppy drive different from the installed operating system.
The Boot Manager also has other functions different from starting your system. They can help you to:
- Display the boot menu.
- Loads system-specific boot loader.
- Move the boot parameters to the boot loader.
- It initializes and configures components like memory and processor.
Suggested Read => Methods to Boot into Windows 10 Safe Mode
Where is the Windows Boot Manager: How to Access it
Windows boot manager is usually located in the System Reserved Partition or the EFI System Partition (ESP).
If your system uses BIOS, you will see it here: \Boot\bootmgr
If your system uses UEFI, you will see it here: \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi
There are different methods you can use to access the Windows boot manager. Though this method depends on the type of your computer, while some systems will accept F8, on another system you will be able to use F12 or Esc to display the Windows boot manager. The BIOS and UEFI settings are the best place to configure your boot options.
Why is Windows Boot Manager Showing up
Below are some reasons why the Windows boot manager keeps showing up:
- The Windows boot manager may display if the boot configuration data is corrupt, so while trying to load the operating system, it will open.
- Whenever there is a hardware or drive change in the system, it may prompt the display.
- Whenever there is a change to the boot configuration, UEFI, and BIOS Settings, it may force the display.
- A recent Windows update may cause the prompt to show.
- When your computer has multiple operating systems installed, then you will get the display.
The BOOTMGR file is a read-only and hidden file that is located in the root directory of the hard drive partition and tagged as Active in Disk Management.
On many Windows computers, we can have this partition tagged as System Reserved and usually do not have a drive letter to recognize it. However, if you don’t have a System Reserved partition, the BOOTMGR will be located inside the primary C:
Further Reading => How to Change Drive Letter in Windows
How to Configure the Windows Boot Manager
#1) How to enable Windows Boot Manager Using Command Prompt
You can enable or disable Windows boot manager bios settings through Command Prompt, but you will need administrator rights to perform this.
1. Enter cmd in the search box, right-click Command Prompt, and select Run as administrator.
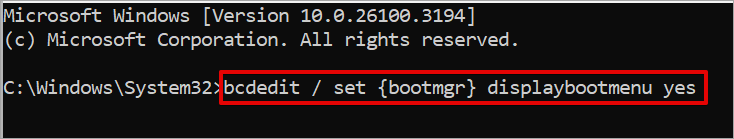
2. Enter the following commands one after the other in the Command Prompt and hit the Enter key. You will get this message “The operation completed successfully”.
bcdedit / set {bootmgr} displaybootmenu yes
bcdedit / set {bootmgr} timeout 30
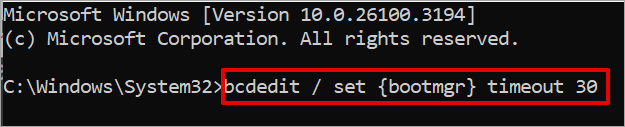
Please note that the timeout you set determines the displaying time for the boot manager.
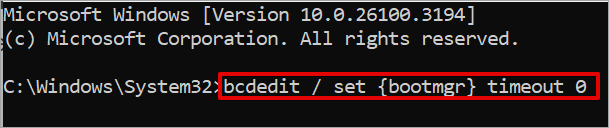
#2) How to disable Windows Boot Manager Using Command Prompt
You will need to type bcdedit / set {bootmgr} timeout 0 and hit Enter.
#3) How to set the Default OS Using Command Prompt?
Type this command bcdedit /default {current} and press Enter to set the default OS.
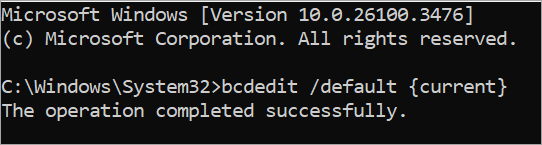
Another command you can use is bcdedit / set {bootmgr} displaybootmenu no command
This command can disable the boot menu in Windows by modifying the Boot Configuration Data to prevent the boot menu from being displayed when the system starts up.
#4) Using System Configuration to Reduce Timeout
Open the Start Menu, search for “System Configuration” and click on it.
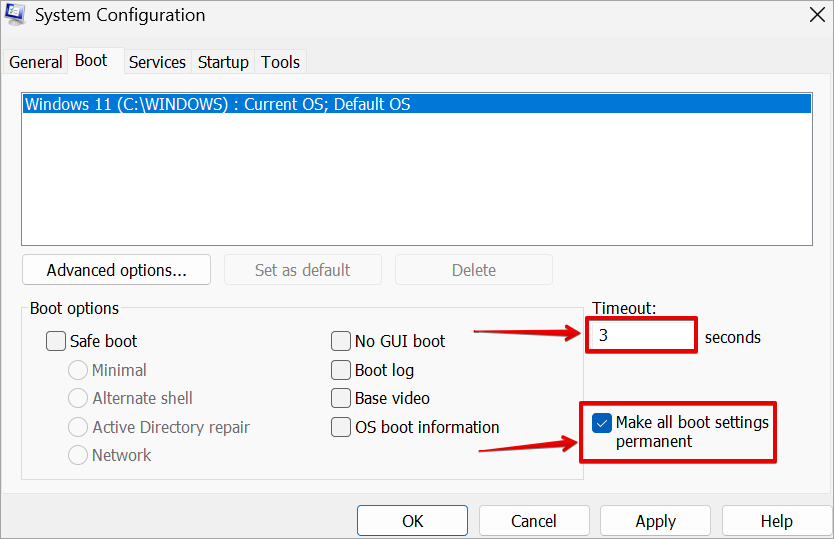
Click on “Boot” tab, Set “Timeout” to 3 seconds, and check the box “Make all boot settings permanent“.
How to Reinstall Windows Boot Manager
When you are getting this error, “Bootmgr is Missing” what this means is that your Windows Boot Manager is malfunctioning because the files are corrupted or missing.
If you want to fix this error, you will use a Windows installation USB/DVD to boot into the Recovery Environment and run the bootrec /fixmbr and bootrec /fixboot commands.
Refer to this video to understand Repair/Recover Windows boot manager (Fix bootloader)
How to Fix Startup Errors with Windows Boot Manager?
- Operating System Not Found Error: This is a regular error users encounter when the Boot Manager cannot locate the operating system. The simple solution to this is to check the boot order in BIOS/UEFI settings and confirm that the right drive is selected.
- Dual-Boot Error: This error occurs when you have more than one operating system and one stops showing on the boot menu, you can use the command bcdedit to reconfigure the Boot Manager.
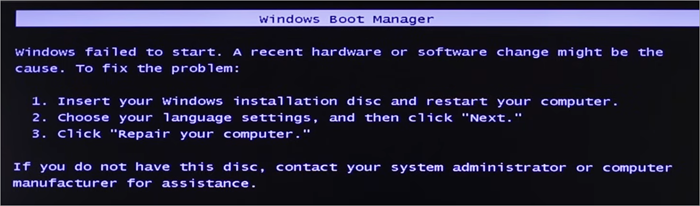
[Solved] Windows Failed to Start A Recent Hardware or Software Change Might Be The Cause:
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I get into the boot menu?
It depends on the computer manufacturer or the motherboard, but the keys usually used to open the Boot Menu are Esc, F2, F10, or F12.
2. How do I fix a missing Windows Boot Manager?
If the error is an operating system not found, the simple solution is to check the boot order in BIOS/UEFI settings and confirm that the right drive is selected.
If the error is a dual-boot error, which usually occurs when you have more than one operating system and one stops showing on the boot menu, you can use the command bcdedit to reconfigure the Boot Manager.
3. How do I resolve Windows Boot Manager?
When on the Install Windows screen, select Next > Repair your computer. When on the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot. When on the Advanced options screen, select Startup Repair. After Startup Repair, select Shutdown. After completing this, you can restart the system and confirm if Windows can boot properly.
4. What is Windows Boot Manager in BIOS?
The Windows boot manager is the first layer of the startup process that runs. It determines which operating system to load. When you select an OS, the boot manager then drops control to the system’s bootloader. This loader loads the operating system’s kernel and everything else needed for startup.
5. How do I manage Windows Boot Manager?
The BOOTMGR displays important information for troubleshooting and resolving Windows boot errors. It is possible to manage the Boot Manager from Advanced System Properties, System Configuration (MSConfig.exe) tool, or Windows command Prompt (BCDEdit command).
6. How do I add Windows Boot Manager?
Type “cmd” in the search box, right-click on the command prompt and select “Run as administrator”. On the command prompt type this: bcdedit /set {bootmgr} displaybootmenu yes and bcdedit /set {bootmgr} timeout 30. After each typing hit the enter key.
7. What happens during Windows boot?
During a normal Windows boot, the boot loader will access the file system on the boot drive. It will launch ntoskrnl.exe, and load the boot-time device drivers into memory. After these are loaded, the kernel launches the session manager smss.exe, which starts the login process.
8. What happens if I delete Windows Boot Manager?
When you remove or disable the Windows Boot Manager, it will not affect your operating system. But when you remove it without setting how your system boots or making sure one operating system installed has been set up for booting, this may cause booting issues on your computer.
Conclusion
We have discussed extensively what Windows Boot Manager can be used for and we also talked about some Windows Boot loader errors and how that can be quickly fixed. We also discussed how you can easily enable or disable Windows Boot Manager using just a single line of command.
When your Windows Boot Manager is having issues coming up, we have shown you the steps you can take to reinstall it again. The Windows Boot Manager function is not just about choosing the operating system that you want your system to boot into, but it is also a very useful resource for troubleshooting different boot issues.










