Quickly identify the defects in Integration & Unit testing with the top Embedded software testing tools. Pick the most secure & reliable software to find and fix the defects during all software development phases:
Embedded Software Testing is crucial in ensuring the software quality, reliability, and as well as Compliance with industry standards. Deciding on the right one purely depends on the project’s requirements and budget, hardware compatibilities, and regulatory requirements.
Manual testing is a bit expensive, prone to errors, and at times difficult to reproduce test scenarios. Tools used for automating software testing will increase the efficiency and save costs, allowing for setting up CI/CD integrations to run tests, which reduces the efforts required to identify the issues/bugs and fix those bugs during the software development life cycle.
Table of Contents:
- What is Embedded Software Testing: Top Tools to Pick
- Basic Terminologies
- Type of Tools for Embedded Software Testing
- Challenges Faced While Testing Embedded Software
- List of the Best Embedded Software Testing Tools
- Comparing the Top Tools to Test Embedded Software
- Comparing the Prices of Top Tools
- How to Choose the Right Software?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Embedded Software Testing: Top Tools to Pick

Let us first understand a few terminologies used in these Embedded Systems Industries and then elaborate on why Software testing tools are essential and their key features, challenges, choosing the right one, and the future trends in Embedded software Testing.
Basic Terminologies
Embedded Systems: They are the electronic computing systems controlled by someone to carry out specific tasks inside a larger system.
Embedded Software Testing: It is also a special category of software testing to check both Software and Hardware in embedded systems to verify that the final product works as per requirements. It is defect-free, focusing mainly on Performance, Functionality, and Dependability of the embedded systems.
These embedded systems are used in many different embedded industries such as automobiles, medical equipment, aviation, machinery, washing machines, ATMs, Railways, the vehicle industry, Military & Defence, and consumer electronics.
Sample Examples in detail for the industries that use embedded systems are:
- Automobiles: Safety measures for systems and their features, engine management, and overall functionality are managed by embedded systems.
- Medical Equipment: Most of the advanced medical centres that opt for MRI machines and other health check-up devices are all dependent on embedded systems to function.
- Aviation Systems: The Flight control systems/electronic systems that are used in Aircraft are heavily relying on embedded systems for controlling flight navigation, monitoring, and communications. Also, these embedded systems help in operating the autopilot functions, providing precise navigation and stability during the flight
Type of Tools for Embedded Software Testing
Embedded software testing tools help identify the defects during software development phases and or unit, integration, and at the whole system level testing. These tools serve as an additional layer to find the defects in the backend processing.
There are mainly 2 types of Embedded software testing tools, such as:
- Static Analysis: Here, the approach is examining and testing the source code before execution to detect defects.
- Dynamic Analysis: Here, the approach is examining the source code at runtime or while it is executing. Monitors real-time behaviour and memory usage.
Apart from the above 2 broad categorizations, there are different types of Embedded software testing, such as,
- Unit Testing: Testing of individual software modules across embedded systems.
- Integration Testing: Making sure, integrated modules are working together correctly.
- System Testing: The entire embedded system is validated.
- Regression Testing: Verifying that new code changes have not introduced new bugs.
- Hardware -in-the-loop (HIL) Testing: Real-world hardware interactions are simulated.
The image below shows examples of embedded software testing:
Challenges Faced While Testing Embedded Software
- Efficient resource constraints to optimize the codebase as lightweight as possible to leverage techniques like code refactoring, efficiency of data structures, and memory leaks. Otherwise, it can hamper the functionality and performance.
- Robust real-time performance, i.e., missing any deadlines, can be a serious incident too. By implementing RTOS (Real-Time Operating Systems) for managing the tasks’ periodization and scheduling any time-critical issues or tasks.
- Hardware dependencies, ie, seamless integration with various other systems, sensors, and control units.
- Ratio of Software & Hardware defects that are identified
- Continuous Software updates like regular Security Fixes, kernel upgrades, and device drivers, which may increase the importance of build and deployment rollouts.
- Reproducible defects
- Most of them are Open-Source Software, which has the probability of a wider range of test combinations and resulting scenarios.
- Cost constraints, i.e, meeting any technical requirements while balancing costs, are a crucial factor for high-performance components that are premium level for consumer gadgets.
- Industry Compliance Standards, be it medical or any automation industry or aviation sectors, several industry regulations and compliance standards are a must, which can be time-consuming and may turn out complex if left unattended at later stages.
- Security Threats, ie, multi-layered security approach and implementation, are a must to avoid any security threats vulnerabilities, including any data breaches and unauthorized accesses.
Considering Future Trends in Embedded Testing
The embedded testing field is continuously evolving, and some of the trends to consider for the future are:
- Focusing on Security
- Increased usage of Automation testing solutions
- Integration of AI and Machine learning into testing tools
- Cloud-based Testing Solutions
There are versatile Embedded software testing Tools available to assist with above mentioned embedded software testing, such as:
List of the Best Embedded Software Testing Tools
- Parasoft
- Tessy-Test System
- VectorCAST
- Perforce Klocwork
- Eggplant
Comparing the Top Tools to Test Embedded Software
MISRA: Motor Industry Software Reliability Association <promotes best-practices, coding standards and guidelines >
AUTOSAR: AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture. <Common framework for Global standard for software, hardware interfaces and methodology>.
CWE: Common Weakness Enumeration < weaknesses list for software and hardware>.
| Embedded Software Testing Tools | Supported Languages & Standards | Automation Capabilities | Certification Support (e.g., ISO, IEC) | Integration with CI/CD & DevOps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasoft | C, C++, Java; Supports MISRA, AUTOSAR, DO-178C | Strong automation for unit, integration, and regression | Yes – ISO 26262, DO-178C, ISO 62304 | Excellent CI/CD integration with Jenkins, Git, Azure |
| VectorCAST | C, C++; Strong MISRA, ISO 26262, DO-178C support | High – unit testing, regression, code coverage | Yes – ISO 26262, DO-178C, FDA (via tool qualification) | Integrates with Jenkins, Bamboo, Azure Pipelines |
| Tessy | C; Supports MISRA, ISO 26262, IEC 61508, DO-178B/C | Good – unit testing and integration | Yes -DO-178, ISO 26262, IEC 61508 | Supports Jenkins & GitLab; some setup effort needed |
| Perforce Klocwork | C, C++; C#, Java , Strong support for CWE, MISRA, CERT C/C++, | It’s a Static Code analysis tool for identifying any compliance issues, security and code quality | Yes – DO-178C, ISO 26262, IEC 61508, | Supports DevOps via plugins; CI tools integration GitLab, Jenkins |
| Eggplant(KeySight/ TestPlant) | C, C++; Especially strong in aerospace & automotive | Designed mainly for UI automation, system validation and model-based testing | Certifications are Customer implemented, used mainly in regulated environments. | Integrates with Jenkins, Eclipse; setup can be complex |
Let’s understand each of the Embedded Software Testing Tools in detail.
#1) Parasoft
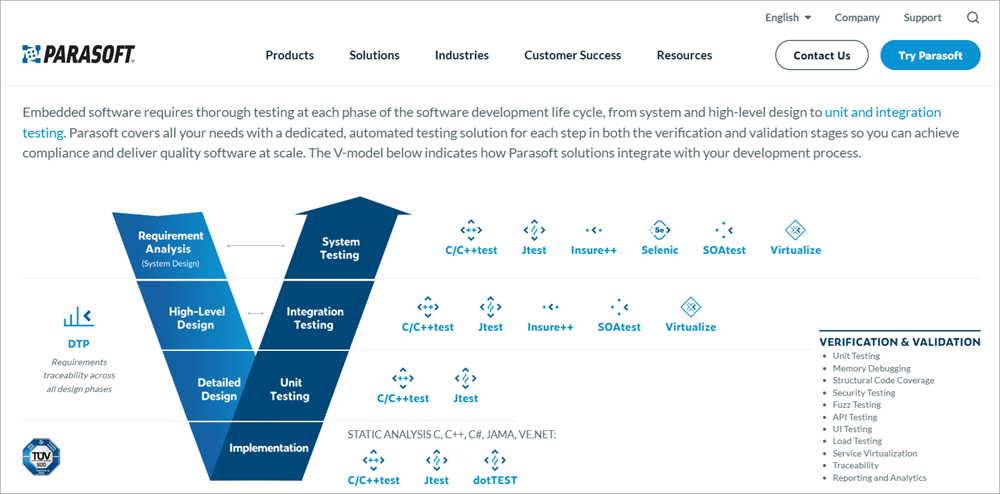
Parasoft tool integrates into any of the development environments and offers reports for statistical data analysis at component level with the help of Parasoft Development Testing Platform (DTP) for testing embedded applications, also provides automation of continuous development activities in the Integrated Development Environment (IDE) ie, Parasoft DTP contains the tools for code reviews, unit testing code coverage and traceability matrices and even static analysis.
- Provides pre-configured settings for code compliance, which meet the industry and regulatory standards, where Testers can prefer to customize the Parasoft templates to achieve the user’s needs.
- Dynamic Analysis: Can monitor applications during execution time and identify runtime errors like buffer-related overflows, memory leakages, and null pointer exceptions.
- Does Static Code analysis
- Regression Testing: Automatically identifies any regression errors that are found after code changes
- Integrates with CI/CD pipelines seamlessly with GitLab, Jenkins, and other automated test scenarios.
- Have the capacity to support the targeted hardware with cross-compilers effectively.
- Ensures industry standards compliance is in order with safety-critical features testing. Safety-critical standards like :
- EN 50128(Railways Industry)
- DO-178C(Avionics Sector)
- ISO 26262 (Automotive sector)
- IEC 61508(Industrial related)
Pricing: The starting price is approximately $55,800/year
Website: https://www.parasoft.com/industries/embedded
#2) Tessy-Test System
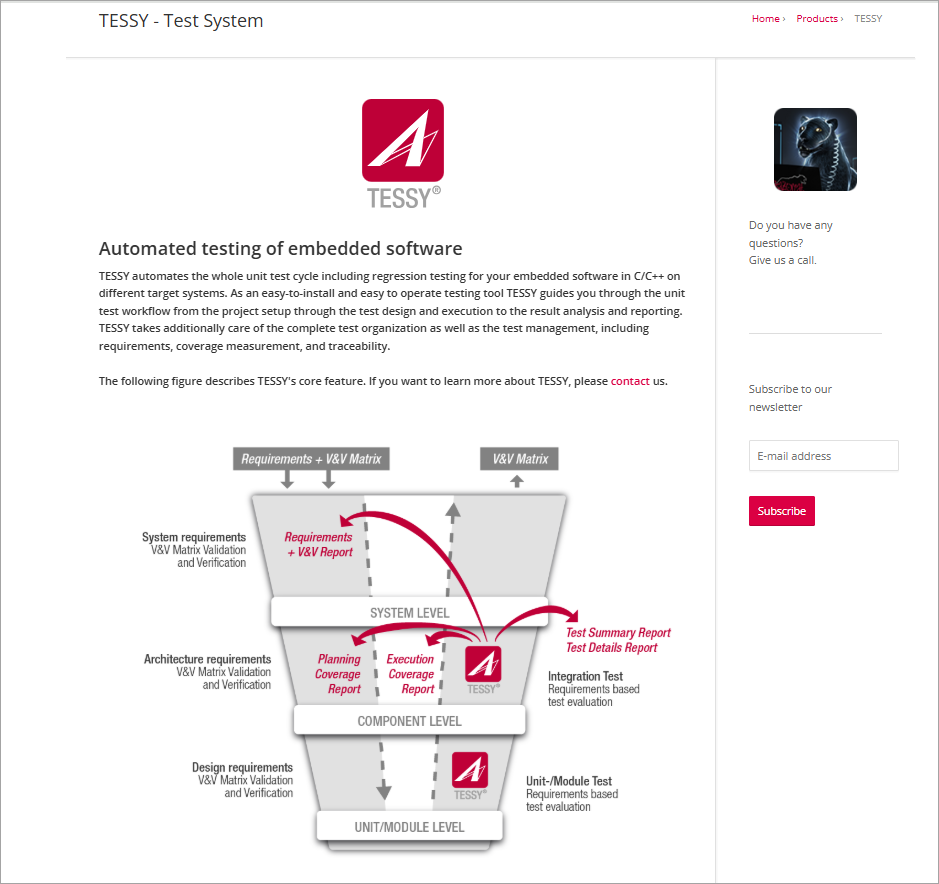
Razorcat core technology has developed a powerful unit testing tool called TESSY for C-code modules, which supports the most relevant compiler environments, microcontrollers, and target platforms.
TESSY is a Test System that automates the entire unit test cycle, including regression testing of embedded software in C or C++ on various embedded systems.
- TESSY is an easy-to-install and operate testing tool that guides throughout the unit testing workflow, i.e, from project set up through the test design and test execution until test results analysis to reporting.
- It has additional features that facilitate the whole QA cycle from project set up, design, execution, test management, including requirements analysis, measuring the coverage and traceability matrices.
- It is best suitable for Safety-critical applications such as Aerospace, Medical, and automotive industries.
- Assists projects needing automation, traceability, and tool qualifications.
Pricing: You can get a quote for pricing details.
Check this video on Unit/Integration Testing with Tessy:
Website URL: https://www.razorcat.com/en/product-tessy.html
#3) VectorCAST

Vector Software has many products, and Vector Software’s primary product is ‘VectorCAST’. VectorCAST is one of the embedded software testing platforms used to automate testing activities during the development lifecycle, particularly used for safety-critical applications. Vector CAST is specifically designed to support any commercial-level real-time operating system.
Vector CAST/C++ is a highly automated test solution for unit and integration testing used by embedded developers during the validation of safety and business-critical systems within embedded systems.
One of the Vector CAST products, called ECU testing tools, is helpful to support in implementation of test environments and simulations in a very efficient way.
From SIL Simulation to HIL (Hardware-In-the-Loop) testing, along with functional acceptance testing, Vector CAST testing tools are providing re-usable and scalable solutions regardless of the development process tasks. Doesn’t matter if your ECU is intended for a vehicle with an internal combustion engine or purely electric vehicles, or a hybrid version.
Here are the features for C and C++ for Unit and Integration testing:
- Supports a wide variety of Simulators, Compilers, and processor architectures
- Supporting the Windows and Linux platforms
- Supports C++14,C++11 and C++17
- Supports Host and Embedded Target Testing or Simulator
- Full command line interface facility
- It automates the regression testing phase
- Has integrated solutions for,
- VectorCAST/Ada
- VectorCAST/C++
- VectorCAST/QA
- TESTInsights
Advantages:
- Easily works well with existing software development tools.
- Continuous and collaborative testing is enabled
- The main focus is on the embedded systems
- Provides the most automated tools.
- Different Application Areas Vector CAST is dynamically & widely used below sectors:
- Aerospace
- Railway
- Medical devices and equipment
- Automative
- Financial Industries
Pricing: You can get a quote for pricing details.
Check the video below for more info on how the Automation for C and C++ unit testing is done:
Website: https://www.vector.com/gb/en/products/products-a-z/software/vectorcast
#4) Perforce Klocwork
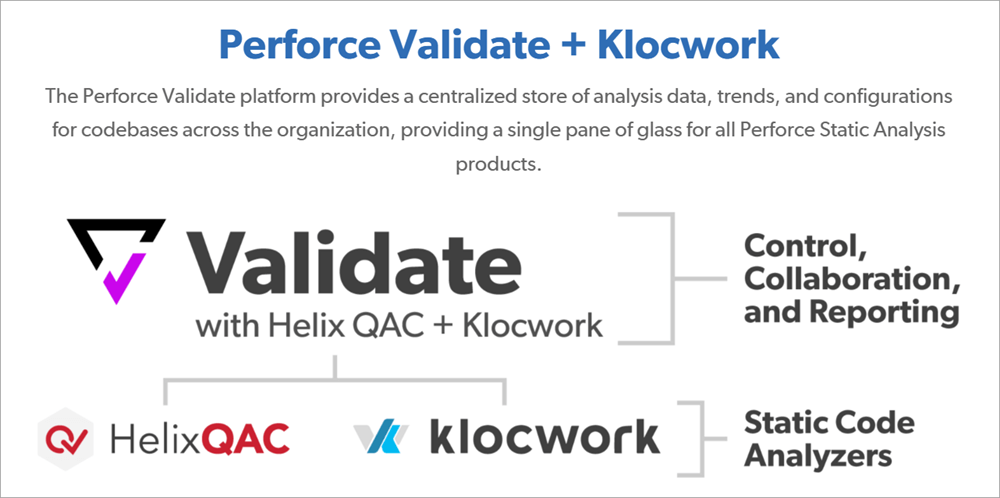
Perforce Klocwork insight has become part of Perforce Software Inc. It is a static code analysis tool and yet powerful tool used for enhancing the quality and security of embedded software systems. Perforce Klocwork is widely utilized in industries where compliance and reliability are critical, such as Finance, Aerospace, telecommunications, and automotive sectors.
Perforce Validate Platform offers a centralized store of analysis of data, configurations, and trends across the organizations for codebases, perforce single pane for all Perforce Static Analysis Products.
Klocwork is certified for ISO(Automotive), IEC(General Industry & Medical devices), and EN(Railways) Compliance with key functional safety standards.
Perforce Klocwork is considered one of the best Static Analysis and SAST(Static Application Security Testing) tools for accelerating the delivery of quality code and time-to-market releases for C, C++, C#, Java, Python and Kotlin, and JavaScript. Also, it is built for enterprise DevOps and DevSecOps and offers a 7-day free trial to get started.
- Offers IDE integrations
- Dashboard creation and reports actionable insights features.
- Scalability: Capable of handling large sets of codebases without impacting the performance.
- Automated feedbacks when integrated with CI/CD pipelines.
- Works smoothly with GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins, etc.
- Identifies the security vulnerabilities, potential bugs, and any compliance issues, if any, early in the development lifecycle.
- Static Code Analysis: Supports coding languages like C, C++, C#, Python, and other coding languages too.
Advantages:
- Collaboration improvements teams find it helpful by enforcing standard coding practices.
- Enhanced security breach prevention
- Early identification of issues during the development stages, rather than addressing them after the development
- Quality Assurance checks- by making sure the built software follows the compliance standards and also meets the industry-specific quality checks.
Pricing: It offers a flexible pricing model
Website: https://www.perforce.com/products/klocwork
#5) Eggplant (TestPlant)
Eggplant (Test Plant) is a GUI-based, Model-based, and AI-powered automation testing tool. It was acquired by Keysight Technologies and is broadly focused on software test automation and not particularly for embedded systems. Eggplant is versatile, and its capabilities stretch to checking on APIs, user interfaces, entire systems, and databases, making sure the coverage is comprehensive.
Eggplant tool excels in embedded systems automation testing process, and it has a unique approach in image recognition and Machine Learning (ML) to interact with the examined solutions just like a human being would be doing, and allowing it to function across any operating systems and devices.
In order to ensure the robustness and reliability in critical applications effectively, Eggplant can simulate across several network conditions to carry out the examinations of embedded systems in different scenarios and different environments.
- The eggplant test provides extensive coverage.
- Speeds up the release cycles and optimizes user experiences.
- Improves the quality assurance process.
- Easy-to-use solution, secure and discover much faster, which tests any kind of software on any platform and device.
- With AI-powered exploratory testing, you can produce actionable insights.
- With a low-code testing tool, which is driven by user Interface (UI), development can be streamlined.
- With the scriptless testing model, maintenance costs are much reduced.
- Using Eggplant, you can find defects much faster, accelerating release cycles, streamlining the regression testing, and improving testing accuracy & software quality.
- Eggplant focuses mainly on load and performance testing of embedded Systems/ applications to make sure they operate effectively and efficiently under stress.
Pricing: The price starts at $2,500/month.
Website: https://www.keysight.com/us/en/products/software/software-testing/eggplant-test.html
Comparing the Prices of Top Tools
| Tool | Starting Price | Licensing Model | Short Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parasoft | ~$55,800/year | Customized | Comprehensive automated testing suite. |
| Tessy | Not publicly listed | Customized | Specialized in unit and integration testing for embedded systems. |
| VectorCAST | Not publicly listed | Customized | Supports multiple programming languages for embedded testing. |
| Perforce Klocwork | Flexible pricing | Fixed/Floating licenses | Static code analysis with support for various coding standards. |
| Eggplant(KeySight/ TestPlant) | $2,500/month | Subscription | AI-driven test automation across multiple platforms and technologies. |
How to Choose the Right Software?
Choosing the right Embedded testing tool involves more comparing features, and it’s all about matching your business goals and specific technical stacks and their needs with the right resources and capabilities. It is equally important to ensure choices you make will seamlessly align with your requirements and the company’s resources to drive this testing process/phase effectively and efficiently.
Hence, these AI-powered testing tools are chosen wisely to empower the teams to succeed.
The selection of the right Embedded software testing tools depends on various factors such as:
1. Project Budget
Considerations on ‘Cost and Licensing’ is a must when selecting software testing tools, like:
- Is the chosen tool Open Source or Commercial?
- Whether or not the pricing will fit into your estimated budget and project requirements
- Ensure if there are any subscriptions involved or just one-time license fees.
2. Project Requirements
Testing requirements and their scope in the project should be well planned. Common criteria to check are:
- Can the tool handle Hardware-in-the-Loop(HIL) testing and real-time constraints?
- Does it need automation or just manual, or needs both types of testing activities?
- Main things to check are whether does tool supports Unit, integration, system, and regression testing phases.
3. Project Team Resources/Expertise
Check for learning curve and ease of usage, ie, is the tool easy to set up first and then use by all team members?
- Does it provide community support, and is sufficient documentation offered?
- If required, initial training and technical support are available from the tool’s customer support
4. Integration Capabilities
Check for the ‘Test Automation and CI/CD Integration pipelines facilities’, like
- Verify how the tool supports test automation to avoid manual effort
- whether the version control systems like SVN and GIT et are compatible with
- Can the tool integrate with Azure DevOps, GitLab and Jenkins, and other CI/CD pipelines
5. Industry Standards and Compliance Checks
When working with the safety-critical industry, it is essential to ensure the tool will comply with below standards,
- DO-178C(Avionics )
- ISO 26262(Automative)
- EN 50128(Railway industry)
- MISRA & AUTOSAR (Coding standards for C/ C++)
- IEC 61508(Industrial Automation)
6. Future Scalability Support
- Need to check whether the tool supports the scaling facility, especially if there are larger projects and complex embedded systems involved
- Also, the check tool receives support and regular updates from the providers.
7. Dynamic Analysis and Static Analysis
Static Analysis and Dynamic Analysis capabilities checks are worth considering, like
- Static Analysis helps in identifying code errors, if any, before execution. A check tool offers this
- In order to ensure maximum test coverage, check that the can tool is capable of performing code coverage analysis.
- Dynamic analysis support for detecting any runtime errors, for example, buffer overflows and memory leaks, if any.
Further Reading => Best Memory Leak Detection Tools
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the advantages of Automation Testing in Embedded Systems?
• It helps in the faster test execution process
• Likely to have reduced human errors
• Regression testing is efficient
• Time-to-market is faster
• Test coverage is increased relatively
2. What is Embedded Software Testing?
Embedded Software Testing is the process of validation and verification of software components that are designed for the hardware systems to ensure their performance, functionality, and reliability in real-world platforms.
3. What different types of Testing are carried out in Embedded Systems?
• Unit Testing: Individual components are tested.
• Integration Testing: Verify the interaction between two components/modules.
• System Testing: Making sure the entire system is functioning as expected.
• Regression Testing: To verify the changes and make sure those changes are not affecting the existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Speed and resource usage are measured in this type of testing.
• Real-Time Testing: Making sure the responses are meeting time constraints.
• Security Testing: Identify vulnerabilities and take measures if any are found.
4. Name a few Safety-Critical Standards in Embedded Software Testing?
• IEC 61508: Industrial Automation Safety
• EN 50128: Railway Software Safety
• DO-178C: Avionics Software Safety
• ISO 26262: Automotive Safety
5. Are there any open-source(free) tools used for Embedded Software Testing?
Yes, there are open-source embedded software tools available, such as,
i) Google Test: For Unit testing C++
ii) Unity Testing Framework: Used for C and is a simple testing framework
iii) CppUTest: Lightweight and used for Unit testing for C/C++
6. What are the main Key Features of these Embedded Software Testing Tools?
Below key features below are worth noting before you choose the Embedded software testing tools:
• Debugging and code coverage
• Protocol compliance testing is supported
• Automation testing support and platforms supported
• Real-time testing capabilities are worth looking for
• Simulations and emulation features are a must to check out
• Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) is Supported. (HIL Testing Tools enhance the embedded software testing and they simulate the real-world hardware environment for the software to test for functionalities and performances without the need for physical hardware, which will drastically reduce the development time and the cost involved.)
7. What is HIL (Hardware-in-the-Loop) Testing?
HIL Testing or simulation is also known by other acronyms like HiL, HWIL, HITL.
HIL testing is a technique for developing and testing real-time embedded systems, including complex systems, in a virtual environment.
Examples where the HIL testing technique can be used for testing embedded control units for vehicles, aircraft, machinery, and power electronics.
Also, in the automotive industry, HIL Testing Technique is used to test the Electronic Control Unit (ECU).
8. What is CAST-32A?
‘Multicore Processors’ is often referred to as ‘CAST-32A’.
Recently, the most significant changes in the embedded systems computing world is the increase in the adoption of Multicore processors. These Multicore processors are to represent the future of the aerospace development process, and their adoption has become a crucial part in order to meet the needs of the modern sought-after avionics systems and also to avoid the potential single-core long-term processor availability concerns, if any.
CAST (Certification Authorities Software Team) has published recent papers on CAST-32A, popularly termed as ‘Multicore processors. These papers identify the different topics involved that could potentially impact the integrity of the airborne software system execution on multicore processors, safety, performance, and provide guidelines intended to guide the production of safer multicore avionics systems.
9. What is SAST (Static Application Security Testing)?
Static Application Security (SAST) is a software testing methodology that is designed for analysing and inspecting the applications ‘ code, source code, and also binaries for coding and designing conditions in order to uncover any security vulnerabilities.
This SAST is also known as “White-Box Testing”.
10. What are Embedded testing tools?
A specialized software testing tool used to test embedded systems wherein software is integrated with hardware to perform dedicated functions is called an embedded testing tools.
These tools are helping to ensure that the software running on processors, microcontrollers, and embedded devices is functioning well, is reliable, and satisfies the safety measures and performance standards.
11. What is an example of Embedded software testing?
A real-time example for embedded software testing includes Automotive industries, Aerospace and Medical sectors, including another practical example like a Smart thermostat embedded system.
Example: Smart Thermostat Embedded System
Functionality: A smart thermostat controls the home’s heating and cooling system based on the user’s settings and environmental factors like the day’s temperature, time of day, and humidity etc.
Embedded Software Testing Example: Typically, 5 types of testing are carried out to test this smart thermostat system, such as,
Unit Testing: To check the individual test function () returning correct values based on temperature settings.
Integration Testing: Verification of the temperature sensors module sends accurate findings to the controlling logic.
System Testing: Running the whole system, to check whether the system responds to on /off correctly when the temperatures differ.
Static Code Analysis: This is carried out to identify any memory leaks and any coding standards violations.
HIL Testing (Hardware-in-the-Loop): Simulating the temperature sensors to make sure the software responds by adjusting the heating system at home.
12. How to test embedded software without hardware?
Embedded software testing without hardware is carried out mostly during the early development stage when there is limited access to physical hardware systems, by making use of simulation, virtual devices/platforms, and host-based testing techniques.
For example, to simulate hardware responses, ‘Mock functions and Stubbing’ can replace the hardware-dependent code.
Conclusion
Embedded Systems are nothing but hardware and software integrated to perform specific functionality with a microcontroller, which drives the intended actions.
Modern Embedded Software Testing has lots of challenges than regular software testing, because embedded testing is heavily relying on the hardware environment along with software testing simultaneously (to deal with functional and Non-functional aspects/components).
Hence, it is ideal to adopt embedded automation testing for any robust software testing to handle the issues, to increase the efficiency, to save time, as Manual testing is prone to errors and is expensive & or it’s difficult to replicate manual test cases.
Embedded Software testing is incorporated into every industry, such as Avionics, Automotive, Media, healthcare, High Technology, Logistics & transportation, Sports and Entertainment, Public Services, Education, Financial services, Insurance and intellectual property, and Telecommunications.
Investing the right amount of time and expert-level resources into your embedded testing tools is sure to pay off in the long run, which leads to safer, more reliable, and higher-performing embedded systems emerging into to market be it you are a tester, developer and or project manager.
As the technology is advancing in this dynamic field, it is essential to stay informed and follow the right best practices about the latest trends and tools adopted for embedded systems testing.
Research Process
- I spent 25 hours researching and writing this article so you can have summarized and insightful information on which Embedded Software Testing Tools will serve you best.
- Total software researched: 20
- Total tools shortlisted: 5







