Discover the various challenges and critical security risks involved in IoT Cybersecurity. Learn the various steps to tackle cyber threats and safeguard your enterprise data from cyberattacks:
IoT devices have software, internet technologies, and sensors, and can share resources or data via the internet with other devices with the same abilities.
With IoT, you can remotely operate your household equipment, while industrial companies use IoT technology on their industrial equipment to communicate and share resources. Car owners can also operate and manage their cars remotely through a remote control or phone.
Table of Contents:
Cybersecurity in IoT: Importance & Challenges Involved

Here is the video on the importance of IoT Security:
Types of Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) can be found in homes, industries, and public spaces. Many IoT devices can be used specifically.
- Consumer IoT Device: These devices are used in everyday life, such as home and office appliances.
- Commercial IoT Devices: These are devices used by some organizations to automate their business operations. These are smart devices that can monitor assets and supply chain management.
- Healthcare IoT Devices: These devices help connect patients, doctors, and medical devices, reducing the need for incessant visits to the doctor’s office and hospital.
- Industrial IoT Devices: These are primarily used in manufacturing companies, energy production companies, and many more. Devices like Digital control systems.
What is IoT Cybersecurity
IoT cybersecurity is the practice or process of protecting these internet-enabled devices from malicious or intruder attacks. IoT devices come in different forms, such as smartphones, Office gadgets, Household equipment, Industrial machinery, and healthcare gadgets, all connected to the Internet to share resources with other devices.
Both customers and manufacturers can implement IoT cybersecurity solutions. IoT Security ensures that these devices are fully and adequately protected from intruders, ensuring the enforcement of critical security policies that protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access or control of the IoT devices.
[image source]
AI-Driven IoT Security
Artificial Intelligence will play a pivotal role in the security of the Internet of Things. AI will significantly improve security. One benefit is that the AI algorithms can analyze large data generated by IoT.
With the AI mechanism, there will be predictive maintenance of the device, automated and real-time threat response, predictive maintenance, and rapid anomaly identification. In the future, AI algorithms will be further trained on how to enhance and boost IoT security.
Edge Computing Security Style
In the future, IoT security will rely on the security style that edge computing is designed with. We will have IoT Edge devices with low latency, improved response time, and data processing within the source, reducing the rate of MiTM attacks and responding to threats in real-time.
Implementation of Blockchain Technology
In the future, there is expected to be more reliance on blockchain technology to boost cybersecurity in IoT. This technology can help decentralize the system and ensure data integrity.
Zero-Trust Security Model
This is one of the best security models available. It follows a simple rule of not trusting anything (device) or any users. The key component of this model is the restriction placed on access; there must be user and device verification.
Quantum-Resistant Security
Cryptographic algorithms protect our data and privacy and keep us safe online, but the invention of powerful quantum computers can now crack the encryption that keeps us all safe and alive. A quantum-resistant algorithm that can help fight and protect against quantum computers’ attacks on IoT devices needs to be developed.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Changes to the current compliance and regulatory requirements are expected soon. These changes will support the security of IoT devices.
It is expected that there will be more security awareness and training for individuals, companies, and governments on the proper security practices for protecting data and privacy on IoT devices. These practices include using strong passwords for your IoT devices and how to detect vulnerabilities.
Types of IoT Cybersecurity
- Regulatory Compliance: Individuals and companies must comply with standards and regulations. You will align the IoT device with legal and industry standards.
- Physical Security: This ensures that IoT devices are protected from unauthorized access to the IoT Device location and physical attacks
- Cloud Security: This Secures every cloud infrastructure that supports IoT technology.
- Authentication and Authorization: This helps control IoT device access. Create a strong password, avoid weak passwords or hard-coded passwords, and use multi-factor authentication.
- Endpoint Security: This secures all the endpoints between the IoT devices and other network resources.
- Data Security: This protects stored and transmitted data on IoT devices.
- Device and Network Security: This helps to protect the network and devices against unauthorized access and malicious attacks. It secures communication between IoT devices and other systems.
Different Forms of IoT Cybersecurity Threats
#1) Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
A malicious person may try to disrupt normal IoT operations, by trying to exploit vulnerabilities in the system and flooding the IoT systems with false requests that may overwhelm the system and make them unresponsive to positive requests, thereby disrupting crucial business operations that could lead to financial and reputational losses.
#2) Botnet Attacks
Attackers hijack IoT with poor security networks and now use them to create sophisticated botnets that can be used for different malicious activities like spamming, and DDOS attacks and they can spread more malware on a global scale.
#3) Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
When an IoT security network is poorly configured, an attacker tends to hijack or eavesdrop on what is going on within it. This vulnerability allows them to collect sensitive data for their malicious act. This attack has caused severe financial and reputation damage to organizations.
#4) Malware Attacks
Malicious software attacks on IoT devices are on the increase. Malware can quickly spread to all devices on the network, thereby compromising the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IoT devices. Let’s assume there was a ransomware attack on IoT devices. This type of attack would make the device unusable, and there could be a payment demand before it can be functional again.
#5) Credential Attacks
Avoid the use of weak or default passwords, this is one vulnerability that an attacker looks out for. They believe that once they can gain unauthorized access to an IoT device or network, then they can conduct malicious activities like changing the IoT configuration settings, setting up sophisticated botnets, stealing sensitive data, and many more.
#6) Firmware Attacks
An Attacker should not be able to access the IoT firmware; once they do, they can drop backdoor malware that will always give them unauthorized remote access and control over the entire IoT operation.
#7) Side-Channel Attacks
An attacker uses a side-channel strategy on the IoT mechanism by observing what goes on within, collecting relevant information, and then analyzing the information leakages in the IoT device during operation. These attacks can expose some very sensitive data, like encryption keys and many more.
#8) Encryption Attacks
Data encryption is a critical security measure that must not be negated but be taken seriously because it’s one of the best ways to protect sensitive information in IoT. It helps to secure every communication between IoT devices, other network resources, and users. Never allow an intruder to conduct encryption on your IoT device.
#9) Brute Force Password Attack
Never use a weak and default password for your IoT device. Attackers are always looking for password vulnerabilities within a system. Several software can generate many password combinations to carry out a brute-force attack. Once an attacker successfully performs this attack, he can steal confidential data and conduct other malicious activities on the system.
#10) Physical Attacks
It is very important to have physical protection for IoT devices that are crucial to an organization’s daily operations. Once a malicious person gets hold of essential IoT he can cause physical damage to it, which may cause the device to malfunction and cause business operation breakdown.
Why is Cybersecurity Important in IoT
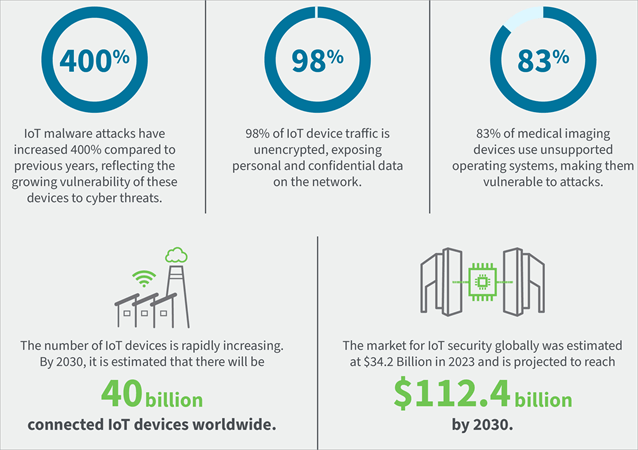
Cybersecurity is very important, considering the benefits IoT devices bring to individuals and organizations. The current amount of IoT shows a higher risk of malicious attacks, such as unauthorized access and data breaches.
One major use case for IoT today is the capability to house extremely sensitive information. Just one unauthorized access or system hack could disrupt an organization’s entire network operation. If a malicious person discovers an IoT has a weak network mechanism, he will retrieve intelligence or cause physical damage to the entire network.
Implementing and enhancing a strong security posture and measures is very important to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IoT Devices. This process ensures and creates a safer and more reliable IoT ecosystem.
How to Enhance Security Measures for IoT Devices
Due to the high rate of the use of IoT, there are new security risks and challenges that warrant deep knowledge of different defense strategies that can be used to effectively address the problem.
The following ways are different ways individuals and organizations can enhance security measures for IoT devices:
- Security Enhancement Systems: Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) that can quickly alert you against malicious attacks on your IoT Device. Deploy Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) to prevent network-based attacks. A security information and event management (SIEM) system can also help you get security attack logs.
- Adding Security Features: Some IoT devices have the capacity for security add-ons to be added to them. This security feature can help encrypt stored data and the one that flows between devices. There must be an authentication process implemented on the device to protect against unwanted device access, which can also help control connections to the device. Adding this feature will help to partition IoT traffic so that it can be easily controlled and managed.
- Follow Security Standards and Guidelines: Organizations like OWASP and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have published many cybersecurity standards and guidelines for users and manufacturers of IoT devices.
- Device Visibility: Individuals and organizations usually lack visibility into what is going on in connected IoT devices. Sometimes, a stranger or employee may connect unauthorized objects to an IoT device, exposing the device to attack. An inventory of all IoT devices on your network is needed so that appropriate endpoint security can be deployed.
- Implement Zero-Trust Policy: When your IoT devices can be accessed on the same network as other network resources, they can be a potential vector for malicious attackers to exploit. The solution would be segmenting or separating the IoT devices from the general network that contains other non-IoT Devices and implementing a zero-trust policy on the IoT network.
- Implement Updates and Patch Management: Regularly install updates and conduct patching management. This is done to fix any IoT device that has vulnerable software and firmware.
FAQ’s on IoT and Cybersecurity
1. What do you mean by Internet of Things?
Internet of Things or IoT are devices with software, internet technologies, Sensors, and can share resources or data via the internet with other devices. These devices can be controlled remotely through the internet access on these devices.
2. What is the purpose of an IoT?
The main purpose of IoT is to create an environment where things connect to share resources. Sophisticated technology can control and monitor this connection.
3. How does the issue of cybersecurity relate to the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things devices can connect through the Internet, which is the backbone of cyber-attacks. The Internet of Things increases our vulnerability to cyber-attacks and the need for defense strategy.
The number of Internet of Things devices now available is now on the increase and creating jobs that need cybersecurity professionals to provide security guidance.
4. What is security in IoT?
IoT Cybersecurity is the process or practice of protecting IoT devices and the network they are connected to. Its main purpose is to protect the confidentiality of data and users’ privacy and confirm that the IoT environment functions properly. It is the process of protecting these devices and making sure they do not introduce threats into a network.
5. How does IoT affect cyber security?
Despite all its benefits, IoT can be vulnerable to network attacks like spoofing. Software or firmware vulnerabilities installed on an IoT device can compromise a complete system. A firmware update can distribute malicious content and steal user credentials.
6. What is the difference between cyber security and the Internet of Things?
Cybersecurity is the study of using technology to protect networks, data, and devices from cyber-attacks or hacking. The Internet of Things (IoT) is what is used to refer to all devices that are connected via the Internet and need to be secured through cybersecurity.
7. Why do IoT devices pose a cybersecurity risk?
IoT devices if not properly secured can be exploited due to weak security configurations. Some of the security challenges facing IoT are weak encryption and zero or insufficient updates.
8. How can we mitigate IoT vulnerabilities?
One major way to mitigate vulnerability in IoT is by regularly Updating software/firmware on the IoT Device. Individuals and organizations can implement an approach that can systematically implement new security patches or firmware updates.
Conclusion
The impact of IoT on our lives and future cannot be underemphasized. This technology is essential and offers immense benefits, but it also has its share of enemy exploitation.
This means that the IoT benefits need not blow us away, but it is very important to implement strong security measures to preserve the integrity and privacy of data within this ever-growing IoT environment. The number of devices that are connected to the 5G network worldwide is increasing and creating the possibility of cyber threats.
Please note that we can only harness the full potential of IoT if we protect our data and privacy. The future of IoT and cybersecurity is bright, and the collaboration of these two is very important to create a safe environment for our smart devices.
We need to always prioritize security in every phase of IoT development and deployment and use available technologies to help maintain a proactive approach to threat detection and response.











