Delve deep into the types of Cybersecurity reconnaissance along with a list of Reconnaissance Prevention Tools. Explore the various techniques involved in it along with simple examples:
Initially, the word reconnaissance was used a lot in the Military. This process or method has been successfully used to win many military combats.
Reconnaissance might be a typical term to most of them, but it plays a pivotal role in Cybersecurity. Reconnaissance might be of any type, but its importance is widespread in today’s world of cyber attacks and threats.
Table of Contents:
- Cybersecurity Reconnaissance: A Must-Read Guide
- Reconnaissance Definition
- Example of Reconnaissance
- Purpose of Reconnaissance
- Use Cases of Cyber Reconnaissance
- Techniques to Perform Cyber Reconnaissance
- What Happens After a Criminal Conducts Reconnaissance
- Types of Reconnaissance Attacks
- How Do Reconnaissance Attacks Work
- Why is Cyber Reconnaissance Important
- How to Detect Reconnaissance Attempts
- How Businesses Can Protect Themselves From Reconnaissance Attacks
- Fundamentals of Reconnaissance: Key Principles
- Different Sources of Information for Reconnaissance
- Top Reconnaissance Prevention Tools
- FAQs on Reconnaissance
- Conclusion
Cybersecurity Reconnaissance: A Must-Read Guide

Reconnaissance Definition
In the military sense, reconnaissance is gathering valuable intelligence from an area or a specific target. Cyber security reconnaissance is just gathering information on your target, such as an individual or another organization.
The objective of this task is to search for any vulnerability in the system and also which would be the best way or more conducive towards an attack.
Almost all successful attacks on the target begin with cybersecurity reconnaissance performed by the attacker. Security professionals can also use it to evaluate their level of security and they can quickly tighten their end to protect against attacks.
Example of Reconnaissance
Some examples of reconnaissance are:
#1) Passive footprinting reconnaissance: This is a form of reconnaissance that involves gathering detailed information about a target without directly contacting the target system or network. This precedes the actual scanning of the system for any potential vulnerability.
Here is the video on Footprinting and Reconnaissance:
#2) Scanning Reconnaissance: This is the scanning of a target network or system for vulnerabilities. The attackers use some tools to scan the host system or network.
#3) Enumeration Reconnaissance: It is the gathering of information or details concerning systems or targets and can, hence, be used in the preparation for an attack on the host. Footprinting and scanning immediately precede this process. It forms a crucial stage for identifying specific vulnerabilities and weaknesses that can be exploited within a network or system.
#4) WHOIS Lookup Reconnaissance: This technique can get information about the registered domain names and IP addresses. Attackers may utilize this tool to gather information for attacks, while cybersecurity experts use it to protect sensitive data. They also enable them to discover who is behind suspicious domains.
#5) DNS Lookups Reconnaissance: This is a reconnaissance or cybersecurity assessment that is done by gathering critical information through the use of this technique. The DNS records retrieved can indicate about its structure and the vulnerability within.
#6) Phishing: This technique exploits the use of deception to extract useful data or intelligence from a victim. Thus, experts can leverage this method to implement periodic security awareness so that they can better trickle down the security posture within their organization.
#7) Social Engineering: This is an attacker’s technique or method to get information about a host target through manipulation and deception. Just like an attacker, cybersecurity pros can use this method to train employees of an organization in the best way, and all can act as a defense against any attack lurking around their organization’s network.
Purpose of Reconnaissance
The main intent of reconnaissance is to find out and gain the information necessary for major decision-making processes and eliminate probable attack vectors and vulnerabilities that an attacker might use.
In contrast, during reconnaissance, the attacker gathers data about his target and tries to avoid being detected by his target’s security tools.
Use Cases of Cyber Reconnaissance
#1) Vulnerability Assessment: The security teams perform reconnaissance to identify the weaknesses within their systems or network that a rogue could exploit, and this can be remedied very well.
#2) Cybersecurity Awareness: Through social engineering and phishing attacks, employees learn how to defend themselves against such an attack.
#3) Penetration Testing: Ethical hackers study reconnaissance to understand the infrastructure of a target system and identify vulnerable spots before attempting to penetrate all of them.
#4) Threat Intelligence Gathering: It is a one-way organizations can gather data on potential threats, phishing campaigns, and emerging vulnerabilities to more effectively prepare their defenses. The incident response preparation can enable any organization to understand the threat vectors and tactics that any particular threat actor may use to develop a truly effective incident response plan in case of an attack.
#5) Regulatory Compliance: Some entities may engage in cyber reconnaissance activities merely for the sake of ensuring that their systems are compliant with relevant laws and standards. They identify improvement domains to avoid regulatory penalties.
#6) Third-Party Vendor Assessment: Organizations ought to validate and assess the cybersecurity posture for any third-party vendors they engage in their services to mitigate risks that are introduced by supply chain dependencies. The security posture of your third-party vendor must be really strong before you can deal.
Techniques to Perform Cyber Reconnaissance
Cyber reconnaissance has different ways of collecting data from the public data domain that may in this case be passive reconnaissance or direct interface or interactions with the target, which can be called active reconnaissance.
Passive techniques are used to check data to have a complete view of a target, whereas active techniques penetrate or examine systems and networks for a better, more detailed understanding of what is vulnerable. These actions or work, when done with a positive intent, are called penetration testing. Malicious actors may also use them in executing a cyber-attack.

What Happens After a Criminal Conducts Reconnaissance
All the information gathered after reconnaissance will be put into the exploitation of the vulnerabilities found, including exploitation like hacking, phishing, and malware.
Each one of these phases in reconnaissance always determines the impact, scale, and sophistication of subsequent attacks. Early prevention or detection of these phases goes a long way in reducing the risk of future exploitation and harm.
Types of Reconnaissance Attacks
#1) Passive Reconnaissance Attack: This is the stage of gathering the essential information in a non-detectable manner because, during information retrieval, it does not directly interact with the target systems or networks. The aim is to gather maximum meaningful information without the target noticing it.
This attack may be performed in the following ways:
- Open Source Intelligence: This shows the collection of data that is openly available like IP addresses, WHOIS records, DNS, social media profiles, employee data, corporate websites, blogs, press releases, legal documents, etc.
- Google Dorking: Special search queries expose sensitive information that has been inadvertently exposed to the internet, including internal documents, confidential code, and even password files.
- Social Media Profiling: Scraping useful information about employees, technologies, and internal processes from LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, etc.
- Shodan Search: Devices and services exposed to the Internet that include IoT devices, webcams, and servers.
#2) Active Reconnaissance Attacks: This is the attack in which the attacker himself interacts directly with the target system or network. This might send up security alerts via an Intrusion Detection System set up with the host system. The intention herein is to probe for security gaps within the target system through direct interaction.
This can be done in the following ways:
- Port Scanning: The target network is scanned to show which applications and services are running and which of its ports are open using an aid such as Nmap or Masscan.
- Service and Version Fingerprinting: It identifies and fingerprints services like HTTP, FTP, and SSH, among others, to look out for known vulnerabilities coming from a source such as CVE.
- OS Fingerprinting: It describes identifying the target computer’s operating system through packet analysis and other distinct peculiarities of network responses.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Done by Nessus, OpenVAS, and Nexpose among others, that scan for known vulnerabilities on an enterprise basis and probably proactively.
- Ping Sweep: A process of sending ping requests to one or more contagious ranges of IP addresses in search of the host that is active on the network.
#3) Social Engineering Reconnaissance Attacks: This is an attack wherein an attacker deceives people to disclose their sensitive information for his benefit. Most of these sorts of attacks have been based on the exploitation of human psychology by taking advantage of the confidence of people in another person.
This attack can come in the following ways:
- Phishing: This is where the attacker sends fake emails or messages to trick users into revealing sensitive information about usernames passwords or other credentials.
- Spear phishing: This is a form of phishing attack, in which, through the reconnaissance process, the attackers use the information they gather to create emails that are a replica of the original email from an individual or organization.
- Pretexting: In most cases, an attacker will impersonate or fake an identity to gain a person’s trust, such as IT support. Such individuals will create some kind of story to have the employees leak sensitive information.
- Baiting: This is just a good example of luring a victim to download infectious files upon visiting infected sites, promising free software, discounts, or content access.
- Vishing: This can be performed through calls like a fake voice call from your supposed bank or IT support requesting you to reveal information. This attack can also be termed voice phishing.
- Tailgating: The unauthorized access to a secure area through the act of following an authorized person through a pretentious reason of forgetting their access card.
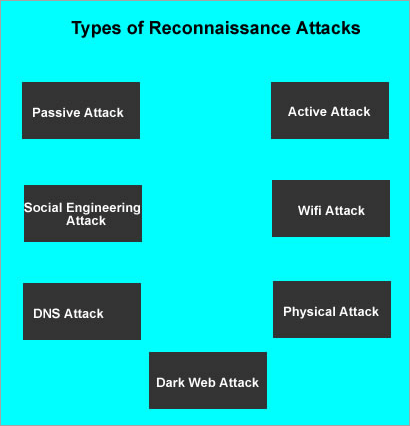
#4) Wi-Fi Reconnaissance: This is an attack where information about the wireless network resources utilized by a target is gathered. In most instances, wireless networks have always presented easy targets compared to wired networks. The motive is to disclose several unsecured or poorly configured wireless networks that permit unauthorized access.
This can be done for example:
- Wi-Fi Sniffing: This is the interception of traffic in a Wi-Fi network. In this context, this may include, but is not limited to, private communications, credentials, and network configurations.
- Wi-Fi mapping: This is kind of a gray area whereby one physically walks to discover the badly configured insecure wireless networks, and then a variety of vulnerabilities are exploited, such as using weak encryption or misconfigured access points.
- Evil Twin Attack: This is the setup of a Wi-Fi access point that is fake which lures or deceives targets to connect and the malicious actor can now intercept their credentials, which can be used for attack.
#5) DNS Attacks: This process collects data about the target DNS Configuration settings. The focus is on getting to know the network structure of the target system.
This attack may be done in the following ways:
- DNS Zone Transfer: DNS zone transfers happen when an attacker requests a zone transfer on poorly configured DNS servers to reveal the whole DNS records of a target domain, subdomains, and mail servers.
- DNS Interception: A technique carried out in man-in-the-middle style intercepting or manipulating DNS requests and responses with the view to routing traffic to malicious servers.
- DNS Enumeration: This involves the use of various tools to enumerate sub-domains affiliated with a target domain. Sublist3r or DNSdumpster could be an example of such tools.
Also Read =>> Fix the ‘DNS Server Not Responding’ Error in Windows 10
#6) Physical Reconnaissance Attack: This is the process of spying on the target’s physical environment to gather some very critical information. The intention is to uncover vulnerabilities that would help in carrying out a cyber-attack.
This attack may be done in the following ways:
- Dumpster Search: A physical search at the dump sites for sensitive information, such as network documents, employee information, and access credentials.
- Monitoring: This is the process of monitoring the target’s physical facilities like the offices and data centers in other to discover weaknesses in their network system.
- Shoulder Surfing: This is a social engineering process whereby the attacker looks over the shoulder of their victim to view their screen and keypad to get their personal information that will help to successfully attack their victim.
#7) Dark Web Attack: This is termed as a process utilizing the dark web for pre-attack intelligence, whereby the attackers obtain sensitive data and stolen credentials that will enable them to move forward with the actual attack on any target.
This attack may be done in the following ways:
- Dark Web Search Engines: These search engines run searches on data breaches online. While the search is running, the malicious actor may see valuable data that might attack a specific target.
- Dark Web Marketplace Monitoring: This is the process of checking the black market listings for stolen credentials, protected data, and access to compromised data.
- Forums Monitoring: Checking online forums where compromised data can be dropped and can carry out an exploit.
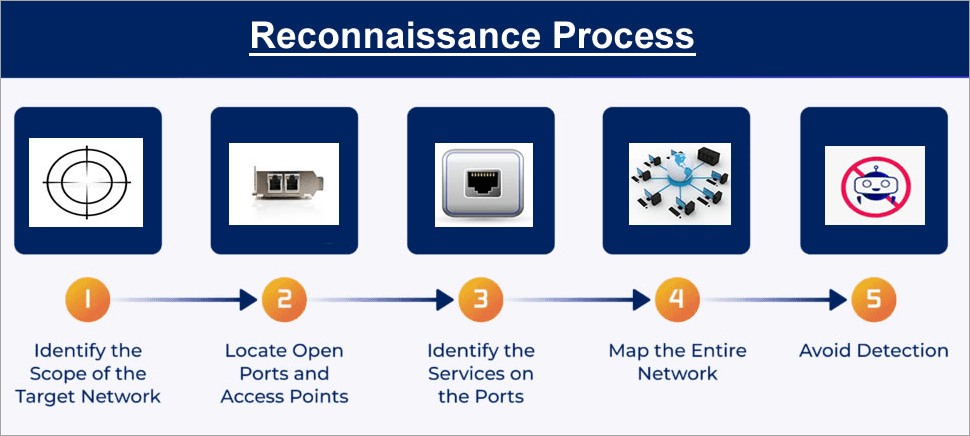
How Do Reconnaissance Attacks Work
Reconnaissance is used for the following:
#1) Gather Information
Information gathering on the target is usually the first phase in any reconnaissance attack. The attacker or intruder or defender is said to be passive in attacking the target at this stage. They will gather this information without your knowledge and use their findings to conduct an attack, or it is something you can use to improve your security posture.
#2) Identify Target
Setting a target range gives the attacker an idea of how big or small a target can be. This will help them on how to execute their plans. While defining this range, they take note of the various areas of your system and network and outline the resources required that make the attack successful.
#3) Identify Active Tools
The attacker searches into your system for active tools and can communicate through those tools to get important information from you. These include email addresses, social media accounts, telephone numbers, and many more.
#4) Identify Open Ports and Access Points
Sometimes, an intruder does not just have easy access to an enterprise network; they find out the access points and open ports they can come in through. They do port scanning that allows them to find open ports and other access points through which they can gain unauthorized access to a system.
#5) Identify the Target Operating System
Each operating system has its mechanism for treating security, each one reinforces this area in a different way from the other. It will thus not be out of place to see an attacker trying to determine what kind of OS he is dealing with. This will help them know how they can bypass any security defenses in place and also know some of the security vulnerabilities specific to a certain operating system.
#6) Running Services Interception
Some running services on your ports may be intercepted by an attacker thereby using the authorized access those services have to gain access to your network. Many times they go unnoticed when they are carrying out this act.
#7) Map the Network
Thus far, the attacker inside your system or network has taken full control of your entire network and can launch the attack accordingly as desired. They make use of network mapping to have full visibility of your network, which may help in locating and retrieving your critical data.
Why is Cyber Reconnaissance Important
Here are the main reasons why cyber reconnaissance is so important:
#1) Strategic Planning: It avails malicious actors with information to actualize a successful and effective attack strategy. Without it, it would be so hard for an attacker to carry out an effective attack since he would be blinded by approaches on how to attack a target and may miss some vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be easily exposed.
Key Objectives:
- Identification of weakness: This would allow the attacker to gain knowledge about some systems, applications, or services that can be manipulated. Examples of these are when one uses an older version of certain software, incorrect configuration, or even an open port that may assist in conducting the attack.
- Network mapping: This is the detailed knowledge of how routers, switches, and servers of a target network are interconnected, and its topology. It will provide knowledge to the attacker where important assets, such as databases or servers, and understand how access could be gained or privileges escalated.
- Identify and process intelligence: It deals with intelligence gathering on workforce information, organizational structures, and work procedures of the target.
#2) Concealing Bad Actors: With passive reconnaissance, you can conduct an attack without the knowledge or detection of any security mechanisms set up. Thus, attackers will manage to attain lots of information without ever directly interfacing with the target network. This, in turn, makes it very hard for the defenders and security mechanisms to trace and block the activity of the attacker during this phase.
The techniques followed in passive reconnaissance include the following:
- OSINT: This is the search for publicly available information on websites, social media, and other open-source where there is no real contact that may raise suspicion.
- Shodan Scan: This technique is used to find devices exposed to the internet without even touching the internal network of the target.
- DNS queries: The WHOIS and DNS record queries can be used to fetch important details on a domain’s infrastructure, such as IP addresses, without raising any suspicion.
#3) Resource Optimization: Instead of trying different methods of attack blindly, an attacker may focus on the weakest link that he finds. This is where resource optimization comes in, helping an attacker know where to focus.
Resource Utilization Advantages:
- Early Attack implementation: With prior knowledge, attackers can move to the exploitation phase more quickly, saving time and resources.
- Higher success rate: By attacking known vulnerabilities or poorly protected assets, attackers increase their chances of success.
- Cost-effective: This helps to avoid wasting time on efforts that are unlikely to be successful (such as attacking systems with strong security postures).
#4) Social Engineering and Phishing Attack: Most cyber attacks use the help of social engineering techniques to convince people to disclose sensitive information or give them access to secured systems. This method plays a major role in cyber reconnaissance, helping attackers get relevant personal information about employees, managers, and even customers from this intelligence.
Benefits of the process:
- Employee profiles: Attackers can use LinkedIn, Twitter, or even a company website to find out details about employees’ responsibilities and positions in the company. This helps them craft more phishing emails for target attacks.
- Internal processes: Getting information about workflows and other internal tools can help attackers pose as trusted sources and appear legitimate.
- Targeting High-value Individuals: Cybersecurity Reconnaissance helps attackers identify people with high privileges, such as System administrators, HR employees, or top-level executives. These people are usually the primary targets of spear phishing attacks.
#5) Testing Defenses and Vulnerabilities: Reconnaissance provides an attacker the chance to test the effectiveness of a target’s defenses before he launches a large-scale attack. The attackers can identify which defenses are poorly configured or weak through information on network services, open ports, and firewall configurations and could then take advantage of those vulnerabilities.
For instance, the attacker can do port scanning to identify the services that are available publicly; if they find a vulnerable service like, for example, an unpatched Apache server, they would concentrate their resources on the exploitation of this service.
Types of Security Gaps:
- Outdated or unsupported software containing known vulnerabilities.
- Any poorly configured firewalls, routers, and applications.
- Portals that have weak credentials that can easily be subjected to brute-force attacks.
#6) Future attacks and threats: Cyber reconnaissance is not done just once whereby attackers can keep monitoring targets over time and sometimes even adjust methodologies under new information at hand. Particularly true in the case of Advanced Persistent Threats, where an intruder attempts to achieve long-term access to target systems.
The benefits of this step include the following:
- Multiple attack vectors: Attackers sometimes may not kickstart an attack immediately. They may spend weeks or months gathering information and discovering multiple ways to compromise security.
- Continuous monitoring: With cyber reconnaissance, you can monitor infrastructure changes, such as new software updates or personnel changes, that may affect the next stage of the attack.
#7) Testing Security Posture: Attackers are not the only ones who make use of cyber reconnaissance. We have the network defenders too. When you have a proper understanding of what cyber reconnaissance is will serve as the beginning of a proper defense strategy.
A suite of various security exercises and pen tests can be emulated about the reconnaissance activities of the red teams, which assist an organization in finding out the possible attack vectors and hardening its defenses in advance.
Benefits for Defenders:
- Predict Attacker Strategies: This would help the security teams to understand how attackers do information gathering and guard against common tactics of reconnaissance.
- Early Detection: By monitoring the different phases of cybersecurity reconnaissance like anomalous scans and DNS queries, defenders can help detect the attacker before they can exploit the vulnerabilities.
- Threat Intelligence Improvement: Security teams study various techniques and tools used by the attackers for improvement in respective detection, response, and mitigation efforts.
How to Detect Reconnaissance Attempts
The following are different ways to detect this:
#1) Looking around for unusual network scanning activity
We can refer to this method as one of the most common activities conducted during reconnaissance. Malicious actors perform their evil acts using tools like Nmap to scan networks for open ports, services, and vulnerabilities within a network. Early detection is key and you can proactively block any attacks before they find vulnerabilities they can exploit.
Look for the following:
- Unusual port scanning: Scanning a wide range of IP addresses or ports is a red alert that shows a reconnaissance attack is currently ongoing. What attackers look for are open ports through scanning and they can check for services running on a target network.
- Port scan patterns: when you sight or observe a series of connection attempts on different ports within a short period is a great sign your ports are currently being scanned.
- Unusual Protocol Requests: When you also sight or observe some unusual request on your protocols like FTP or Telnet points to a scanning job running on your network.
How to detect and defend against scanning activity:
- Through Intrusion detection systems: IDS is a very good tool that can be configured and used to check for any port scanning jobs, unusual network traffic patterns, or scanning of multiple IPs just in split seconds.
- Through Firewall logs: Firewall devices can log unusual access attempts. When you discover connection resets, frequent access requests via some rarely used ports, or multiple connection attempts to the same host within a short period on your firewall is a positive signal that something awkward is going on within your network.
- Through Network traffic analysis: Using tools like Wireshark is a positive step in capturing and analyzing network traffic for unusual scanning activity.
- Through Anomaly detection: The comparison between a normal traffic pattern behavior from abnormal traffic patterns like High volumes of traffic from a single IP source can help expose this underlying attack.
- Through Rate limiting: When you set up a rate limiting on every connection attempt from a single source is a very good method to counter and mitigate the impact of scanning.
#2) Look for banner grabbing or check for service fingerprinting
One way attackers usually collect info about the services currently running on a system is through banner grabbing. This can be achieved by connecting to services such as HTTP, FTP, and SSH and reading the response headers. This method can expose the software versions and other details.
Look for the following:
- Excessive HTTP requests: When you keep seeing rapid and repeated HTTP requests to different endpoints is a very good sign that an attacker is somewhere in the corner of your network trying to harvest banners from your web server or application.
- SSH/Telnet connection attempts: Multiple SSH or Telnet connection attempts may signal banner harvesting or attempts to access your server using standard or weak credentials.
How to detect and protect against banner harvesting or service fingerprinting:
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF is a very good tool for your enterprise network. One very good feature of WAF is detecting and blocking any anomalous HTTP requests.
- Log analysis: You can carefully monitor and observe your logs for any signs of anomalous reactions or requests. Some of these signs include repeated access to a service from unknown IP addresses.
- Service monitoring: We have many service monitoring tools that are very efficient like Nagios and Prometheus which can be used to protect against banner harvesting, which is very good to monitor for unexpected connection requests and service disruptions.
#3) Detect DNS and WHOIS queries
This is one method used during reconnaissance where the attacker finds out the target’s domain name, IP address, and other public information.
Look for the following:
- Excessive DNS queries: A large number of DNS queries to different subdomains or IPs may indicate an attacker is trying to find out infrastructure details about your network or domain.
- WHOIS lookup: A WHOIS lookup will reveal domain registration details such as IP addresses, administrator contacts, and DNS servers.
How to detect and defend against DNS and WHOIS queries:
- Monitor DNS queries: Use DNS logs or monitoring tools like Splunk to detect suspicious spikes in any abnormal DNS queries on a domain.
- Threat intelligence: This can monitor or track fraudulent requests, like when attackers are making WHOIS or DNS queries to your domain.
- DNS rate limiting: To curb DNS abuse, you can set limits on how often DNS queries can be made from a specific source.
- Honeypots: Setting up a DNS honeypot to attract reconnaissance activity and alert you to malicious activity.
#4) Anomalous Login Attempts or Authentication Behaviour
Attackers can use brute force to crack the login information on a system or the attackers may try to guess the login credentials like the username and passwords which may trigger some strange behavior on the system.
Anomalous signs to watch for:
- Failed log-in attempts: When you find abnormally large amounts of failed log-in attempts emanating from the same IP address, this surely points towards a brute-force-type attack.
- Anomalous Account Login Attempts: This happens when you see login attempts into accounts that typically should not have login activity; examples include the service accounts.
- Login attempts at unusual times: Attempts to log in at an unusual time may be indicative of malicious activities, especially if such attempts emanate from areas not normally associated with the activity of your organization.
How to detect and protect against anomalous login attempts:
- Authentication logs: These include analyzing authentication logs that capture the patterns of failed logins. This is true, especially for those trying to use the default password.
- MFA protocols: You can monitor and confirm if the MFA challenges are caused by suspicious login attempts.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems: Through IPS, malicious IP addresses are automatically blocked after some failed login attempts.
- Account lockout policies: Account lockout policies should be enabled after some unsuccessful attempts so that one cannot try brute force on the account.
- Rate limiting authentication: This is the process of restricting the number of requests a user or an attacker can make to a server within a given time period which may be one request per minute or hour.
#5) Anomalous Traffic Patterns or Unusual Activity
This type of reconnaissance activity may generate abnormal traffic patterns, such as checking for specific ports, scanning for services, and excessive data exfiltration attempts.
Check For:
- Anomalous Traffic Volume: When there is increased traffic to certain ports or services, it’s a clear indication that an attacker is scanning your infrastructure.
- Multiple Connections from a Single IP: when you observe many connection attempts from a specific IP address toward different services or ports, it’s a great indication that reconnaissance activities are going on.
- Outbound traffic to suspicious locations: When you see an unusual pattern of outbound traffic going to a specific and suspicious IP address is a great indication that an attacker is preparing for an exploit.
How to Detect and Protect against Suspicious Traffic Patterns:
- Network Traffic Analysis Tools: You can detect anomaly traffic patterns and unexpected connections to public IP addresses by using tools like Wireshark.
- Flow Data Analysis: NetFlow or sFlow is a network monitoring technology that gives you insights into network traffic and performance. It detects traffic spikes or other unusual-looking abnormal traffic.
- Traffic Baselines: This is set up to quickly identify traffic deviations away from normal activity. You can use tools like SolarWinds or PRTG to analyze traffic and detect anomalies.
- Geo-IP Blocking: This is used to restrict scans or traffic originating from a geographical location to another geographical location, like from country to country.
#6) Deploy Honeypots and Deception Systems
A honeypot is a fake system that is disguised to contain sensitive data to deceive and attract an attacker so you can monitor his activities without his knowledge.
How to Detect and Protect with Honeypots:
- Decoy Servers: Set up fake, low-value servers or services that would look like a legitimate server that is part of your infrastructure but are never used in actual business operations. This will attract hackers thinking they are dealing with a legitimate server.
- Early Warning: Honeypots can alert you to an attacker’s first steps, allowing you to detect reconnaissance attempts before they target real assets.
- Tracking Attack Tools: Honeypots will show you the tools and techniques attackers are trying to use, thus giving more insight into how they conduct reconnaissance.
How Businesses Can Protect Themselves From Reconnaissance Attacks
The following are different methods businesses can protect themselves:
#1) Reduce the Amount of Information Publicly Available: The amount of information that an attacker can dig up about an organization determines how successful the planning of an attack might be. Businesses should, therefore, reduce the visibility of sensitive data in publicly accessible channels to make the possibility of a reconnaissance attack very low within businesses.
Action Points:
- Online presence review: Periodically, always audit your company’s official websites, social networks, and job boards for information that is not required or should not be displayed. Remove or restrict the displaying information like employee names, email addresses, organizational structure, and internal procedures.
- Limit domain information: Implement various privacy protection services for WHOIS registrations that mask the ownership and contact details for domains. This prevents attackers from gaining valuable insight into your domain infrastructure.
- Monitor Social Media: Ensure that employees are not giving away too much official or organizational information to the public. Develop social media policies that can restrict the exposure of information concerning your business or organization’s internal systems or security practices on their social media account.
- Data Sanitization: Be sensitive to the type of information shared in the public domain, documents depository, presentations, and press releases. The data should not provide any information related to internal systems, technologies, or infrastructure specifics.
#2) Improve Perimeter Security: Effective network perimeter security is beneficial in that even if the attackers can gather initial information, they cannot easily exploit your system. It involves system hardening of the external-facing systems, thereby deploying active reconnaissance-blocking tools.
Action Points:
- Implement Network Firewalls and WAF: Firewalls are a must for monitoring and controlling inbound and outbound traffic. Proper firewall configuration must be ensured so that unauthorized traffic to sensitive systems and ports is blocked. Utilize WAFs to protect web-facing applications from the most common vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other attacks based on the web.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: These help identify suspicious patterns of traffic that could indicate active reconnaissance activities, such as port scanning or brute-force login attempts. IDS solutions can at least alert the security teams in case of unusual activities, whereas an IPS solution may block malicious traffic.
- Network segmentation: Segmentation is an activity that separates sensitive data and critical systems from the rest. For example, placing sensitive databases on a segmented network behind strict access controls will prevent an adversary from lateral movement once he/she breaches a portion of the system.
#3) Active Monitoring of Reconnaissance Attempts: To effectively stop reconnaissance that involves active scanning, like port scanning or banner grabbing, you need to urgently set up proactive monitoring that can find anomalies before they spread.
Action Points:
- Network monitoring: Network traffic monitoring tools, such as Nmap, are used for finding unusual spikes in traffic, unauthorized scanning, and other abnormal traffic patterns that serve as an indicator for a reconnaissance attack.
- Honeypots: This is a deceptive system setup to divert an attacker’s attention from the main target. Such systems can help detect reconnaissance tools, follow attacker behavior, and gain valuable intelligence on potential attackers.
- Log Management and Analysis: This is the process of using tools and techniques like SIEM to analyze log data to identify anomaly patterns and trends. This tool is in a centralized location to analyze events for malicious activity.
- Alerting and Automation: This is an automatic alert that is enabled and usually triggered when there is a sign of port scanning and other cybersecurity reconnaissance effects. When this is configured will help reduce the impact of the reconnaissance attack.
#4) Hardening of Internal Systems and Resources: Every business should harden its systems so that they can make it difficult for an attacker to gain network access easily.
Action Points:
- Regular patching and updating of systems: when you regularly apply security patches and updates you will be able to protect your system from potential attack vectors. Attackers usually scan for systems that have outdated software, unpatched vulnerabilities, and weak configurations. These are easier to attack.
- Access control: This needs to be implemented in other to minimize access to critical systems by working on the principle of least privileges, which only allows employees to have no more than the minimum access they need for the performance of their tasks.
- Disabling unnecessary services: Disable all services that are not operational and close all the ports not in use. Let us assume the FTP port is not being used then you should make sure that it is disabled so hackers don’t try to use it.
- Strong encryption: Make sure that your data is encrypted at rest and during transit. This will make it hard for attackers to get anything meaningful if they finally succeed in having access to the data.
#5) Training and Awareness for Staff: There is a need to regularly educate employees on current security risks and how to protect and defend themselves against them. They should know that they form part of the security network of an organization. They should know about the below action points.
Action Points:
- Phishing: Attackers make use of phishing emails to trick employees and thereby reveal what is confidential like PII and official details that a third party should not have. Training must be provided to employees periodically to identify phishing emails and suspicious communication.
- Social Engineering: Employees need to be trained on the usage of social media and other online forums. Bad actors use some of these mediums to trick or deceive employees to get information about employees, technologies, and internal systems.
- Security policies: Educate the employees about the company’s policy on data security and protection, password management, and use of company resources. There should be well-defined boundaries of what is acceptable and not acceptable in the policy this will go a long way in reducing the possibility of data leakage or insider threats.
#6) Strong Incident Response Plan: There is always a possibility that an attacker will escape being discovered, gain access, and carry out other attacks on their target. However, a good Incident Response Plan will ensure that your team responds quickly and efficiently in case of a data breach or any other attack.
Action Points:
- Well-detailed Incident Response Plan: The IRP should be properly drafted in such a way that it will capture what to do when a particular incident occurs, like how to quickly remediate current damage. It should also include communication protocols, procedures for escalation, and how any future attack can be managed and mitigated.
- Regular drills: Always have drills like fake attacks to practice the incident response plan in preparation for any real cyber-attack. Periodically perform offensive security testing to test your defenses.
- Post-incident analyses: Immediately after an attack, conduct a post-incident analysis of how the reconnaissance attack was done, what tools were used, and what vulnerabilities in the system made the attack possible. Such analysis will help improve such weak points to prevent further attacks.
#7) Implement Automated Tools: Implement automated tools to assist in the identification prevention, and response against reconnaissance attacks.
Examples of some of the tools to use:
- Nessus or OpenVAS conducts vulnerability scanning to uncover weaknesses that can be urgently remediated before an attacker strikes.
- Nmap and Masscan conduct internal scans to ensure your systems are not open to an attacker.
- Suricata or Snort: This is an intrusion detection tool that can monitor traffic for malicious activity patterns.
Fundamentals of Reconnaissance: Key Principles
The following are key principles that guide effective reconnaissance:
#1) Efficiency and Resource Management
Each successful and effective reconnaissance relies on efficiency. To get the most useful information with the least effort. This comprises employing all kinds of valuable automated tools and using other useful techniques to streamline the reconnaissance process in general.
#2) Avoiding Detection
Another cardinal rule of reconnaissance is that the process must not be detected while performing the process, either the attacker is trying to gain information or a defender is trying to find out an intrusion.
#3) Relevance and Prioritization of Information
Not all information collected throughout reconnaissance is of any good use. The prioritization principle should, therefore, be applied in concentrating efforts on the most important and actionable pieces of information that will help the operation first.
#4) Human Factor
Since social engineering attacks remain one of the key techniques to conduct reconnaissance, even though we have several tools that can scan or collect data, some important information is still gathered by attackers through directly interacting with people or leveraging human vulnerabilities.
#5) Organized Information Gathering
Reconnaissance generally follows steps; thus, it has to be organized and structured. The attackers will always make use of a well-structured strategy for gathering useful information most efficiently. An effective reconnaissance attack usually follows a predictable order in extracting valuable details from the target.
#6) Ethics and Legality
A security defender must know the scope of the task and what is permitted legally which is very critical in other to avoid overstepping boundaries. All types of unauthorized reconnaissance could be termed as unethical hacking or data theft so it must be done ethically and legally because there are legal consequences attached.
#7) Adaptability and Learning
Reconnaissance can be adaptive, attackers will always have to refine their methods at each discovery or change in the target environment. In the same light, defenders need to be adaptive, always changing, and not rigid but also refine their methods as well to best suit the situation at hand, which may make them one step ahead of the attackers.
Different Sources of Information for Reconnaissance
- Human Intelligence
- Physical Reconnaissance
- Technical Tools
- Publicly Available Data Breach Information
- Social Media
- Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Top Reconnaissance Prevention Tools
#1) Imperva
Imperva is a cybersecurity platform hosting a wide suite of security products, from WAF to DDoS protection and even bot mitigation. It safeguards websites, web applications, and APIs from various types of attacks, including reconnaissance.
Features:
- Attack signature databases
- AI-powered traffic pattern analysis
- Application profiling
- Customization
- DDoS protection
Website: https://www.imperva.com/products/data-security-fabric/
#2) SentinelOne
Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native SIEM solution for real-time threat detection, investigation, and response. Aggregating data from diverse sources into one location empowers the use of AI and machine learning to highlight suspicious patterns or abnormalities.
Features:
- Traffic Analysis and Monitoring
- AI-Driven for Anomaly Detection
- Threat Intelligence
- In-Depth Visibility
- Automated Threat Resolution
Website: https://www.sentinelone.com/
#3) Blumira
It is the next-generation cybersecurity solution for proactive threat hunting and prevention of reconnaissance. AI-driven with machine learning, it grants the early detection, analysis, and mitigation of cybersecurity threats before they can cause damage.
Features:
- Traffic Analysis and Monitoring
- Bot Detection and Mitigation
- AI-Driven for Anomaly Detection
- Threat Intelligence
- Automated Blocking and Response
- Seamless Integration and Deployment
- Smart Automation
Website: https://www.blumira.com/
FAQs on Reconnaissance
1. What is cyber reconnaissance?
This is the initial phase of a cyberattack where an attacker gathers information about a target system, network, or organization. Such valuable data is collected to identify any vulnerability or weakness.
2. What are the three types of reconnaissance?
• Active Reconnaissance
• Passive Reconnaissance
• Social Engineering Reconnaissance
3. What is an example of reconnaissance?
• Gathering Public Information (OSINT)
• Scanning the Network for Vulnerabilities
• Deceptive Human interaction
4. What is the purpose of reconnaissance?
• Identify Vulnerabilities and Weak Points
• Understand the Target
• Plan the Attack Strategy
• Map the Target’s Network
• Minimize Risk of Detection
• Obtain Information for Social Engineering
5. What is the reconnaissance method?
Reconnaissance in cybersecurity is the methodology and techniques attackers utilize to gain information about a target as they prepare an attack. This part of the attack cycle mostly forms the introductory phases of an attack cycle for the gathering of critical data that assists attackers in discovering vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the target’s network systems and operations.
6. What is passive reconnaissance in cyber security?
This is a process where an attacker collects information on a target system, network, or organization without any direct contact with the target system.
7. What is active reconnaissance in cyber security?
Passive reconnaissance represents one of the cybersecurity processes in which, through some methods, the attacker gathers fundamental information on the target system, network, or organization without having contact with the target system.
Conclusion
Reconnaissance, whether active or passive, is a very important phase of the cybersecurity kill chain. It gives the attackers the necessary information needed to carry out a successful malicious attack on a network system. When an organization understands the whole reconnaissance process is key to proactive defense, with instant mitigation of all threats discovered.
Organizations should make security policies and enforce them for their employees. They need to apply appropriate security controls, monitoring, and regularly create security awareness for employees which is an anti-dote to reconnaissance
In today’s global world, reconnaissance has become and will continue to be an integral part of cybersecurity. Every organization should know all the different defense strategies they can implement. When they implement this it will greatly enhance their security stand and they can boldly prevent any cybersecurity attacks.




![How to Get Entry-Level Cyber Security Jobs [2023 GUIDE]](https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/wp-content/qa/uploads/2023/10/How-to-Get-Entry-Level-Cyber-Security-Jobs.png)






