Learn everything you need to know about Amazon ECR, including its features, benefits, pricing, and how Amazon Elastic Container Registry securely stores Docker images, in this beginner-friendly guide.
In this Amazon ECR Tutorial series, we are going to cover everything you need to know about Amazon ECR, like what Amazon ECR is, how public and private repositories work, and pushing Docker images and integrating ECR with Jenkins/GitHub Actions for automated deployments.
This guide is the first part of a three-part Amazon ECR container registry series, and the other two are as follows:
Tutorial #1: Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) Guide (This Tutorial)
Tutorial #2: Amazon ECR Public and Private Repositories
Tutorial #3: Amazon ECR Docker Images & GitHub Integration
If you are new to container registries or AWS container services, then this 3-part series will help you build a strong foundation.
You may read through our detailed guide on the Jenkins Tutorial series to gain more knowledge.
Table of Contents:
What is AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR): Complete Guide
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) is a fully managed container registry service provided by AWS that allows users to store, manage, and deploy Docker container images securely at scale.
It easily integrates with Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS), Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS), and other Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) tools, making container image management faster and more reliable.
Amazon ECR supports the creation of private repositories and is integrated with AWS IAM for resource-based permissions, which enables your EC2 instances to access the repositories and container images. Developers can use the Docker CLI to push and pull Docker images.
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) offers security, scalability, and reliability.
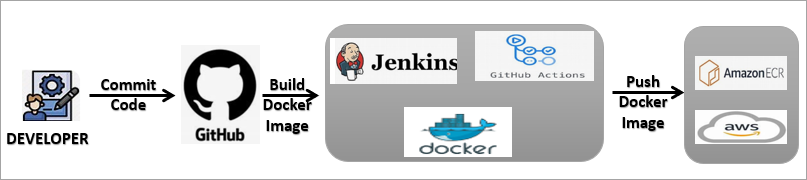
The diagram below shows the workflow for using Amazon ECR.
Features of Amazon ECR
1. Automated Lifecycle Management: Amazon ECR helps in defining lifecycle policies, which, in turn, assist in automatically deleting unused container images, thus ensuring clean repositories.
2. Continuous Image Vulnerability Scanning: ECR allows you to run automatic container image scanning when an image is pushed to a repository, making it easier to track and fix security vulnerabilities.
3. Cross-region and cross-account image replication: With the use of containerized images, replication of the images across AWS regions and accounts can be easily achieved.
4. Pull-through cache for upstream registries: Amazon ECR can be used to cache images from external registries in a private registry, which can then be periodically synchronized.
5. Configurable repository creation templates: You can specify settings such as encryption, immutability of tags, policies, lifecycle rules, and tags to be used by repositories created automatically by Amazon ECR.
6. In-built Container Image Signing: AWS ECR offers an in-built feature of managed image signing, whereby images are automatically given a cryptographic signature during push.
Amazon ECR Requirements (Components)
The following are a few requirements for Amazon ECR
1. Registry access requirements
An AWS account must have access to an Amazon ECR registry to create image repositories and store container images.
2. Authentication requirement
Users must authenticate their Docker client with Amazon ECR using an authorization token generated through the AWS CLI before pushing or pulling images.
3. Repository requirement
Container images must be stored within Amazon ECR repositories, which serve as the primary storage location for Docker images.
4. Access control requirement
Repository policies must be configured to control user permissions and define access to repositories and the images they contain.
5. Image usage requirement
Users must be able to push and pull Docker images from ECR repositories and use those images locally or within Amazon ECS task definitions.
Benefits of Amazon ECR
The following are some of the top benefits of utilizing Amazon ECR
1. Managed and auto-scaling service: Amazon ECR handles the backend work of infrastructure, scaling, and high availability, so teams can focus on application development rather than managing the registry.
2. Effective security controls and compliance assistance: The container image is secured with the help of encryption when it is stored and when it is in transport, IAM permissions, and the sign image feature.
3. Automatic Vulnerability Detection: ECR also scans container images for known security vulnerabilities, which helps to address potential security risks before applications are deployed.
4. Optimized Storage and Cost Management: Lifecycle rules can automatically clean out outdated images that are no longer in use, thus optimizing storage usage and saving costs.
5. Reliable Global Image Distribution: Support for multi-Region replication makes it possible to access container images from various locations.
6. Broad container format compatibility: The AWS ECR supports different types of container-based workloads, including Docker, OCI, and Helm charts.
Amazon ECR Pricing Structure
Here are the key Amazon ECR pricing details:
1. Pay-as-you-go model
Amazon ECR does not require any upfront fees or long-term commitments — you pay based on what you actually use.
2. AWS Free Tier (Applicable Usage)
Private repositories
- 500 MB per month of storage is free for the first 12 months for new users.
Public repositories
- 50 GB per month of storage is always free.
- Data transfer from public repos:
- Anonymous pulls: up to 500 GB/month free.
- Authenticated with an AWS account: up to 5 TB/month free.
- Unlimited free bandwidth when transferring data from a public ECR repo to AWS compute services in any region.
For more details, you can visit the Amazon ECR Pricing Page
As a prerequisite, we will need the AWS CLI to be installed to authenticate with Amazon ECR, and Docker installed as well on any Linux system (e.g., EC2 VM) with access to the Amazon ECR service.
In the following section, we will see how to install AWS CLI and create an IAM Role to Access Amazon ECR.
Installing AWS CLI
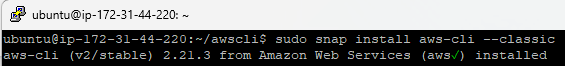
In this section, we will look at installing the latest version of AWS CLI using the snap package manager.
$ sudo snap install aws-cli –classic
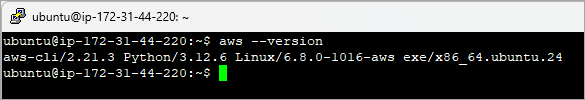
Add /snap/bin to the PATH and verify the installation
$ aws –version
There are other ways to install or update the AWS CLI for your operating system. You can refer to the URL https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html
Create IAM Role to Access Amazon ECR
In this section, we will learn how to create an IAM role to access Amazon ECR & attach it to the EC2 Instance.
We will see how to create an Identity Access Management (IAM) role to provide access to AWS resources with the AmazonElasticContainerRegistryPublicFullAccess policy, which provides administrative access to the Amazon ECR public resources.
The IAM helps administrators to securely control access to the AWS resources, especially for those who have permissions to use Amazon ECR. This also allows you to control who can upload or download images in the Amazon ECR repositories.
Create IAM Role
A role in AWS is an entity that has certain specific permissions. In the AWS Console, search for IAM and click on Roles on the left panel.
Click on Create role.
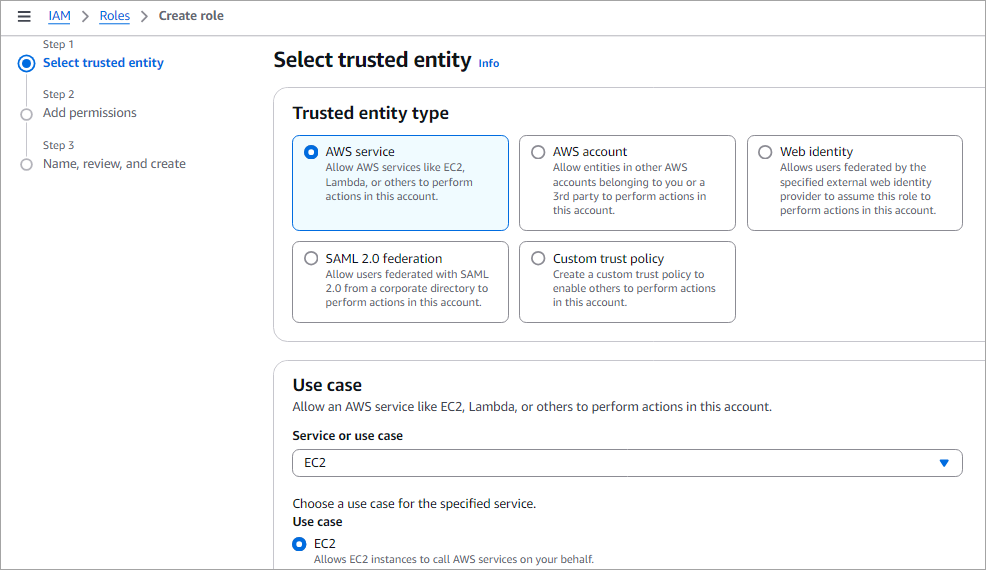
For the trusted entity type, select the option AWS service; for the use case, choose EC2 only, and click on Next.
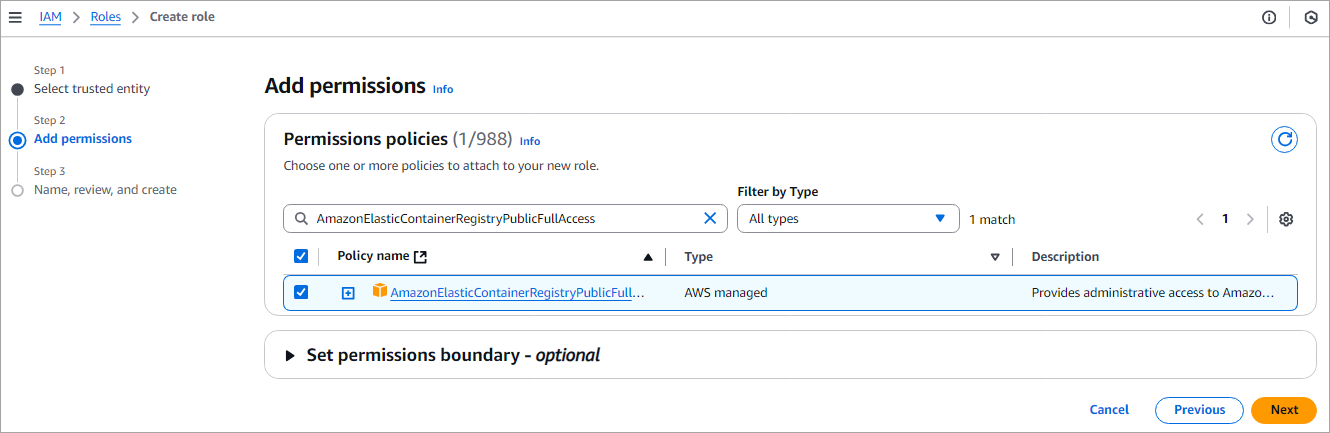
Search for the policy AmazonElasticContainerRegistryPublicFullAccess and click on Next as shown below.
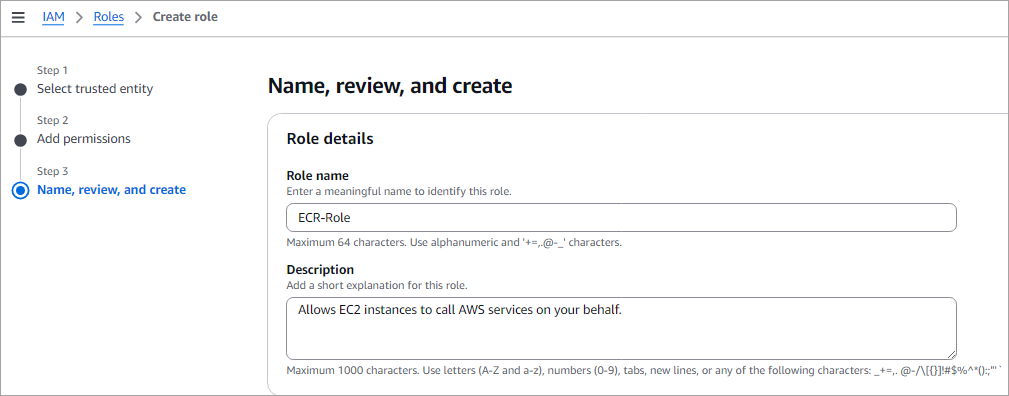
Provide a role name and click on Create role, as in the image below.
The IAM role is now created and listed as depicted in the image below.
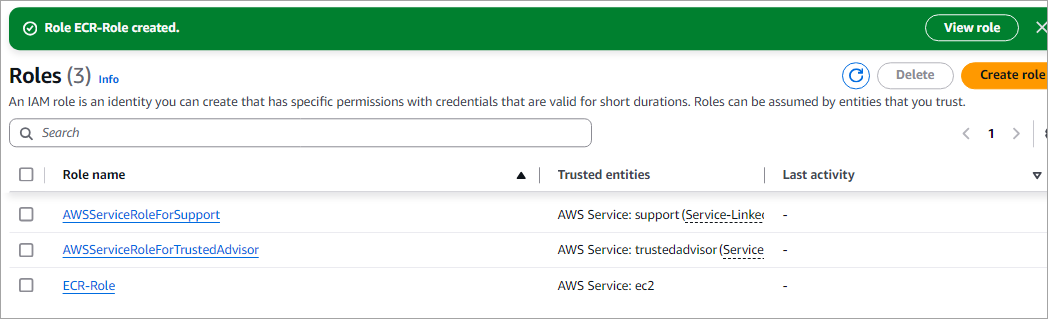
Attach the IAM Role to Your EC2 Instance
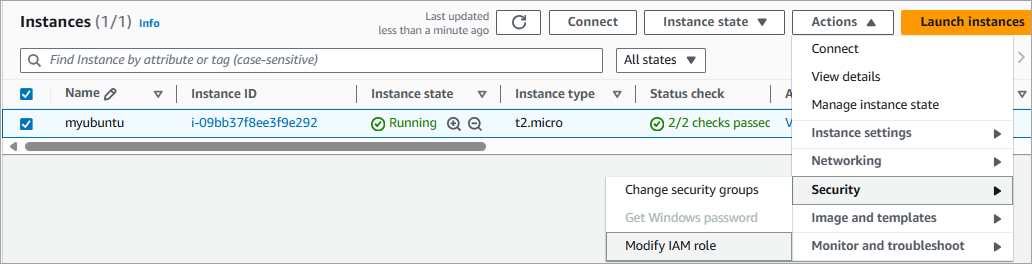
Go back to the AWS console and select your EC2 instance. Select Actions -> Security -> Modify IAM role as below.
Select the IAM role and click on Update IAM role option as shown below.
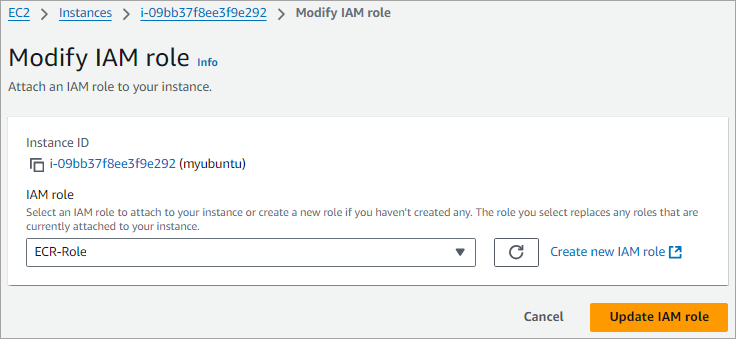
Your EC2 instance can now access Amazon ECR.
Amazon ECR Public Gallery
To pull a Docker image (docker pull) to your local environment, you can do so from the Amazon ECR public gallery, which is a public website to find and share container images. You can browse the container images available @ https://gallery.ecr.aws
For example, to pull the MySQL image, search for it and use the command as shown below.
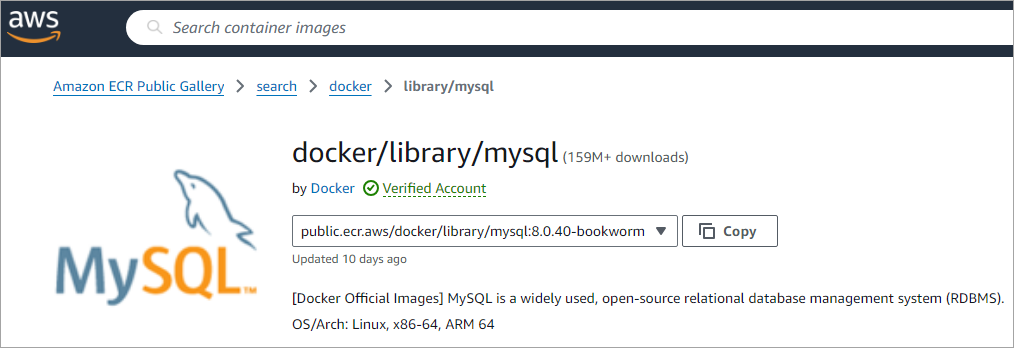
Copy the path shown and run the command below using the Docker CLI.
$ docker pull public.ecr.aws/docker/library/mysql:8.0.40-bookworm
Amazon ECR supports a public registry for hosting container images in a scalable environment. Any repository created in the public registry is available publicly in the Amazon ECR Public Gallery.
Every AWS account is provided with a default public and private Amazon ECR registry.
Sample Node Project and Dockerfile
We will use the node project below and the Dockerfile to create an image and push it to the Amazon ECR repository.
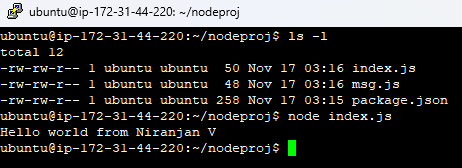
Dockerfile – It is a set of instructions to create an image. Create the Dockerfile below in the same folder.
FROM public.ecr.aws/docker/library/node:lts-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY . /app
CMD ["npm","start"]
Let’s look at the definitions of the commands used in the Dockerfile.
FROM – This command gets the base image from the Amazon ECR Public Gallery.
WORKDIR – To set a working directory for a container.
COPY – Copy files and folders from the local system into the Docker container.
CMD – CMD would run an application when a container is created, not during the image build.
Also, ensure to push the content to the GitHub repository, which will be used in Jenkins integration, and keep your GitHub PAT token handy for authentication in your Jenkins job.
Conclusion
In part 1 of the series, we have seen an introduction to Amazon ECR, which is a Docker-managed container service that is easy to implement to push container images and pull images using no tools or utilities.
It shares and downloads images securely using the HTTPS protocol with encryption, and is fast and reliable to access/distribute your images.
In the next part, we will look at how to automate the Docker Build and Publish of the images to Amazon ECR PUBLIC repository using Jenkins, and also how to automate the Docker Build and Publish of the images to Amazon ECR PRIVATE repository using Jenkins, and also with GitHub Actions in the subsequent part of the series.
Research Process:
This content was created by reviewing official AWS documentation, pricing pages, and service guides to ensure accuracy. Key features, benefits, components, and pricing details of Amazon ECR were analyzed and rewritten in clear, user-friendly language.
Total Time taken to research and complete this Guide: 25 Hours (Approx)
For more quick AWS-related guides, you can explore our range of tutorials below:
- What is AWS S3: AWS S3 Bucket Usage Through AWS CLI
- Jenkins with Docker, Docker-Compose & Docker Swarm TUTORIAL
- Docker Tutorial: Installation And Introduction To Docker
- TOP 30 AWS Interview Questions and Answers
- Best AWS DevOps Tools for Cloud Build and Deployment







